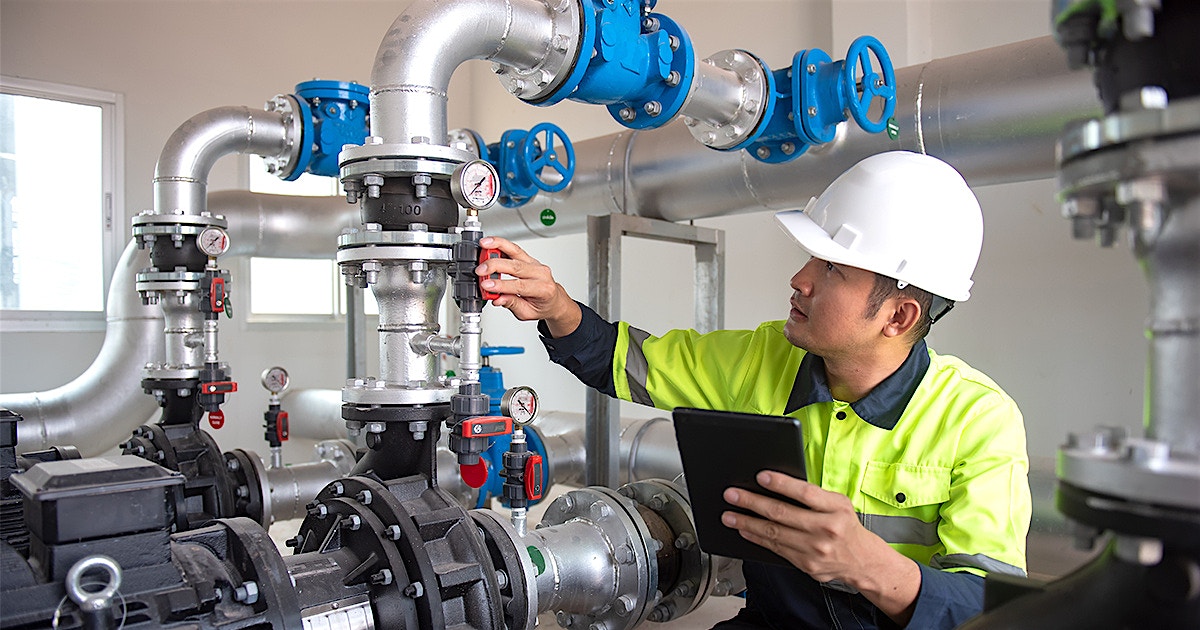
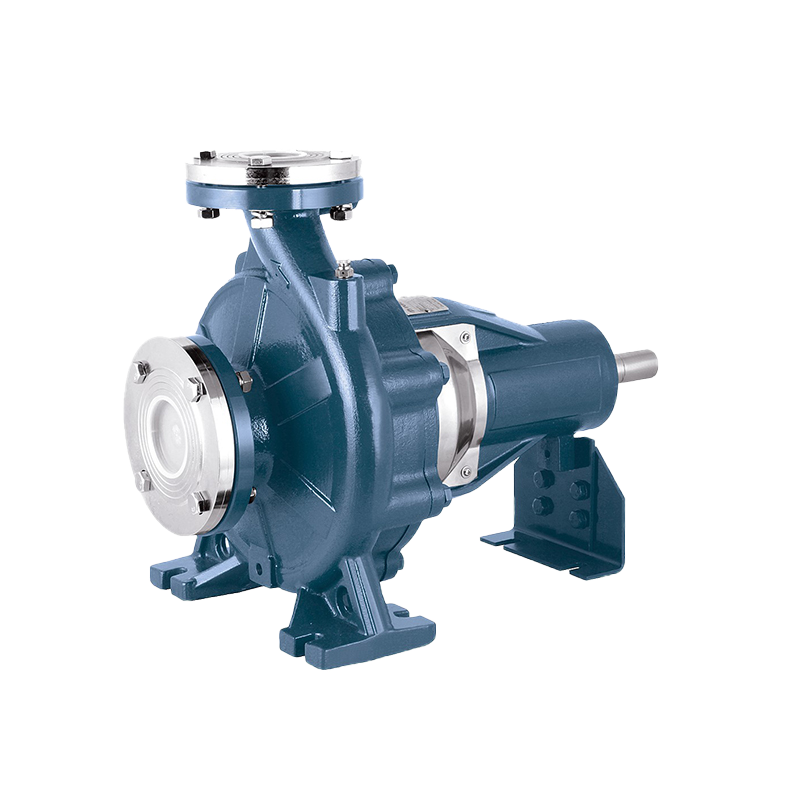
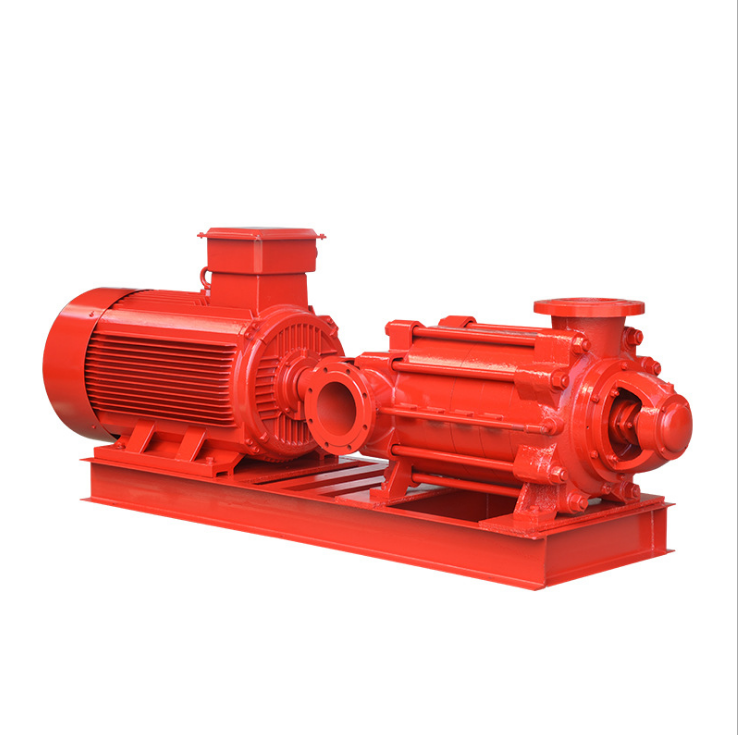
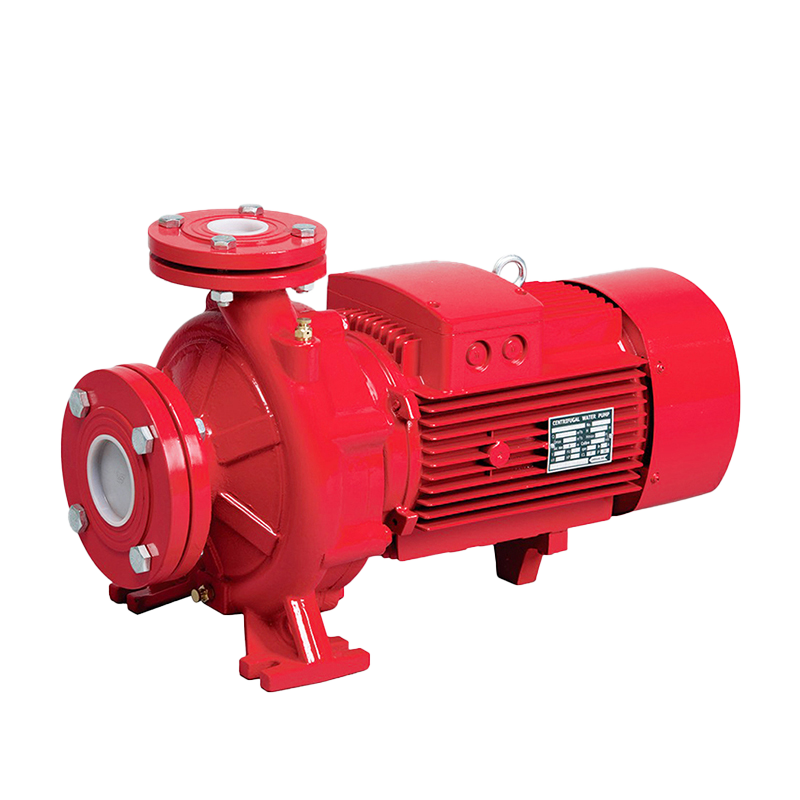
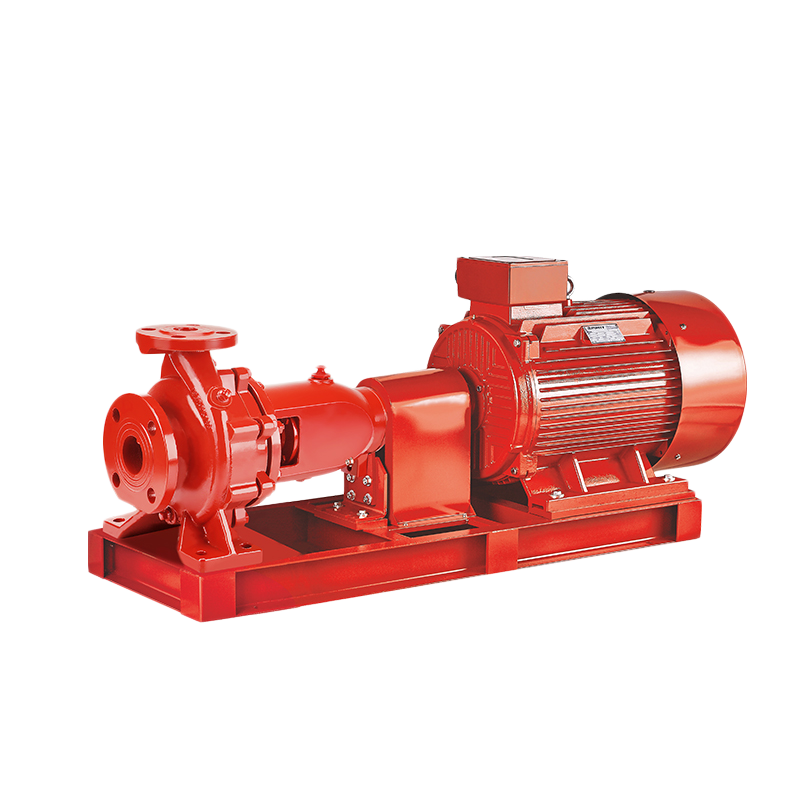
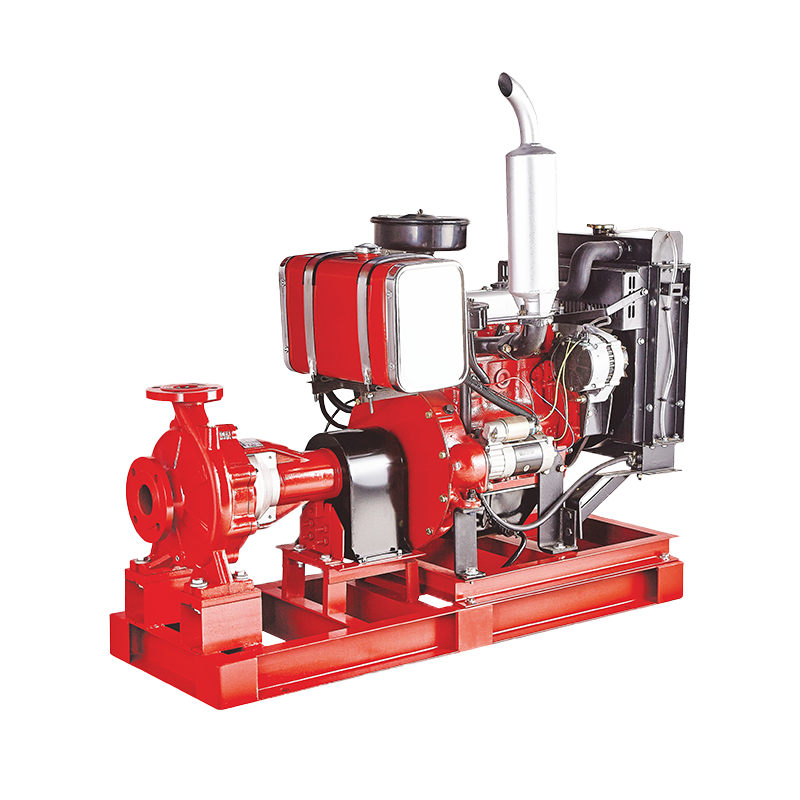
In the world of industrial fluid handling, flexibility and reliability are paramount. Among the various pump configurations available, the horizontal bare shaft centrifugal pump stands out as a versatile and foundational solution for countless applications. But what exactly is it, and why is it so widely specified by engineers and plant managers?
Unlike close-coupled pumps where the impeller mounts directly on the motor shaft, a horizontal bare shaft centrifugal pump features a separate pump shaft supported by its own bearings. This shaft is then connected to a driver—such as an electric motor, engine, or turbine—via a flexible coupling. This “bare shaft” design is the key to its adaptability.
Core Design and Key Advantages
The defining characteristic of this pump type is its independent bearing housing. This design offers several significant advantages:
Flexibility in Drive Selection:
You are not limited to a standard electric motor. The pump can be paired with variable speed drives, diesel engines, steam turbines, or any other prime mover that meets the power and speed requirements.
Simplified Maintenance:
If the motor fails or the bearings need servicing, each component can be addressed independently without dismantling the entire pump unit. This reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
Handling Severe Duty:
The robust bearing frame is designed to handle higher loads, making these pumps suitable for heavier, more abrasive, or high-temperature fluids compared to some close-coupled alternatives.
Alignment Precision:
While coupling alignment is crucial, it allows for fine-tuning, which can extend the life of both the pump and the driver by minimizing vibration.
Where Are Horizontal Bare Shaft Pumps Used?
Their rugged and adaptable design makes them ideal for demanding industrial applications:
Water & Wastewater Treatment:
Transferring raw water, chemicals, and sludge.
Chemical Processing:
Handling a wide range of aggressive and corrosive fluids (when constructed with suitable materials like stainless steel or alloys).
Oil & Gas and Petrochemicals:
Moving crude oil, refined products, and process fluids.
Power Generation:
Serving as boiler feed pumps, cooling water circulation pumps, and auxiliary service pumps.
Mining & Minerals:
De-watering mines and transferring slurry mixtures.
HVAC Systems:
As primary circulation pumps in large heating and cooling systems.
How to Select the Right Horizontal Bare Shaft Pump
Choosing the correct pump is critical for efficiency and longevity. Key selection criteria include:
Flow Rate (Q) and Total Dynamic Head (TDH):
These are the fundamental performance parameters. Always consult the pump’s performance curve.
Fluid Properties:
Consider viscosity, temperature, abrasiveness, and corrosiveness. This dictates material choices (cast iron, ductile iron, 316 stainless steel, etc.) and sealing options (mechanical seals vs. packing).
Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH):
Ensure the available NPSH (NPSHa) in your system exceeds the pump’s required NPSH (NPSHr) to prevent cavitation.
Shaft Coupling & Alignment:
Select an appropriate coupling (flexible disc, gear, etc.) and plan for precise laser alignment during installation.
Efficiency:
For continuous-duty applications, a higher efficiency pump can lead to substantial energy cost savings.
The horizontal bare shaft centrifugal pump remains a cornerstone of industrial infrastructure due to its inherent durability, flexibility, and ease of maintenance. By understanding its design principles, advantages, and proper selection criteria, you can ensure this reliable workhorse delivers optimal performance for your specific application, maximizing uptime and return on investment.
 English
English عربى
عربى
 Fire Pump and System
Fire Pump and System Split Case Pump
Split Case Pump Engine and Pump
Engine and Pump Long Shaft Pump
Long Shaft Pump Multistage pump
Multistage pump Water Supplier System
Water Supplier System Sewage Pump
Sewage Pump Industrial Pump
Industrial Pump Self-Priming Pump
Self-Priming Pump Inline Pump
Inline Pump Domestic Pump
Domestic Pump Electric Motor
Electric Motor Borehole Pump
Borehole Pump