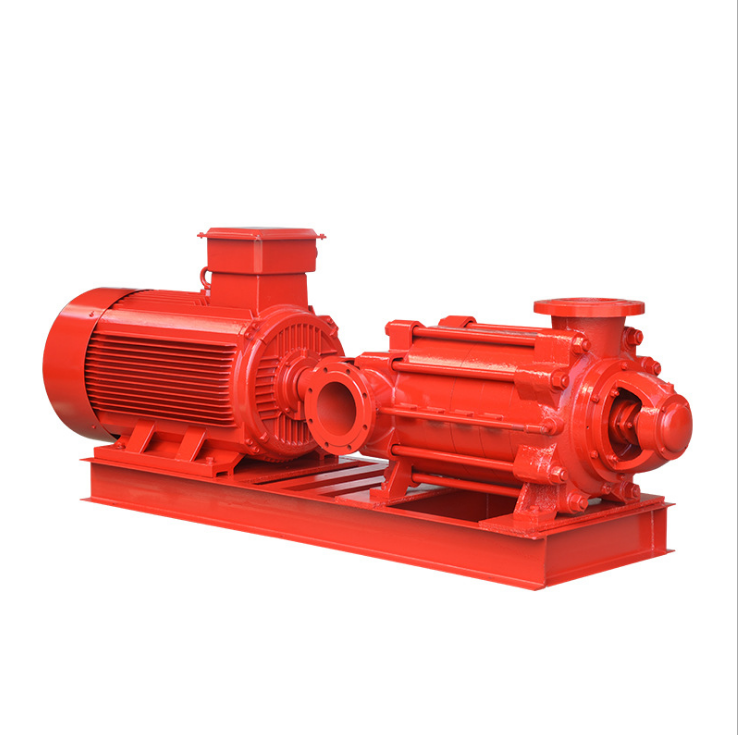
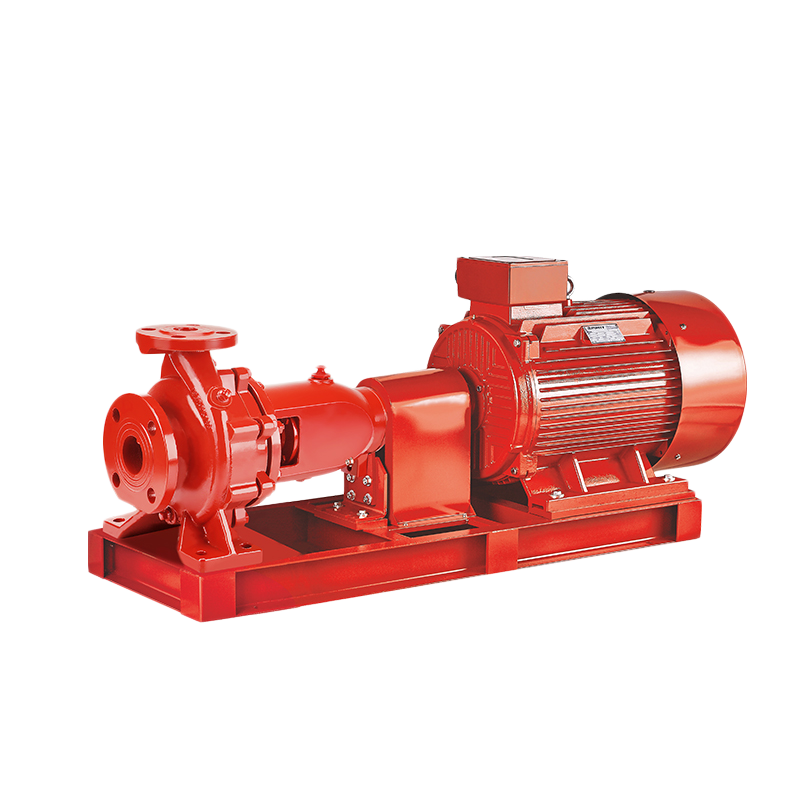
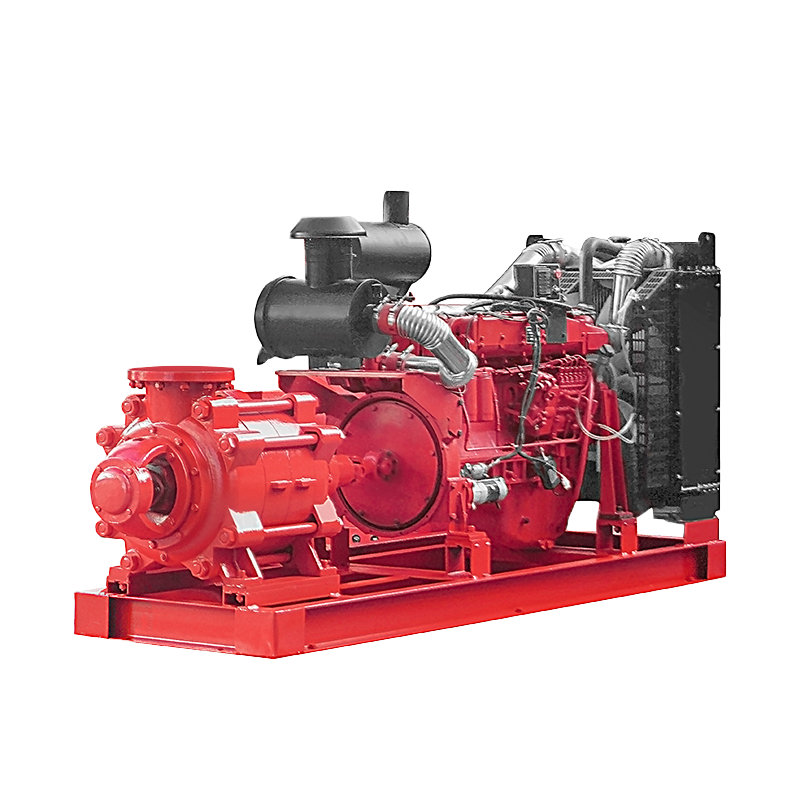
- DN Range of Suction port: 50-400 mm (2"-16")
- DN Range of Discharing port: 32-350 mm (1.5"-14")
- Flow Capacity Range: 4-840 m3/h
- Head/Pressure Range: 19-680 m
- Power Range: 1.5-370 Kw
Diesel engine fire pumps need to be tested at least once a week to ensure they operate efficiently in the event of a fire. To do this, contact the fire pump supplier or an alarm company and request that a representative come out and test the system. The controller can be set to run on a schedule of its own, but it is best to perform a test at a specified interval.
A diesel engine fire pump needs a separate power source. Typically, this comes from the engine's low fuel level switch, hard-wired to the fire pump controller. An engine run contact is also required, and the engine wiring should be sized per the controller's instructions. Installing the pump controller will also require hardwiring a separate power source to the engine block heater.
The diesel engine fire pump should be kept out of the reach of children or pets. The diesel engine fire pump is highly automated, but a human error or malfunction can cause it to fail in its performance. For this reason, the pump house should be staffed with a special person. The person should monitor all parts of the equipment and ensure that they are in working order.
A diesel engine fire pump needs to be installed in a room that is sprinklered and protected from flood waters and external effects. A properly working fire pump can reduce the overall property loss by 71%. However, improper maintenance can decrease the effectiveness of the fire pump. To ensure the safety and efficiency of the fire pump, LionHeart offers fire pump service.
The diesel engine fire pump should be equipped with a dedicated fuel tank. The fuel tank should be aboveground per jurisdictional requirements and be installed within the fire pump room. It must also have a filling system and a visual fuel level gauge. This will ensure that the engine is operating efficiently in case of an emergency.
To use a diesel engine fire pump, it is important to follow the manufacturer's requirements and NFPA 20. The engine must be located in an environment with a maximum ambient temperature of 120 degrees Fahrenheit when the system is at full load and 40 degrees Fahrenheit when it is not. Refer to the manufacturer's datasheet to learn more about the engine's heat rejection capacity when operating. This will help ensure a proper installation of the system.
Diesel engine fire pump systems can be divided into two types. Continuous duty engines are designed to operate continuously for several hours without maintenance, while stand-by engines are designed for short-cycle operation and waiting. In general, a stand-by engine is used for an emergency. A stand-by engine can run for several hours without problems before needing to be serviced.

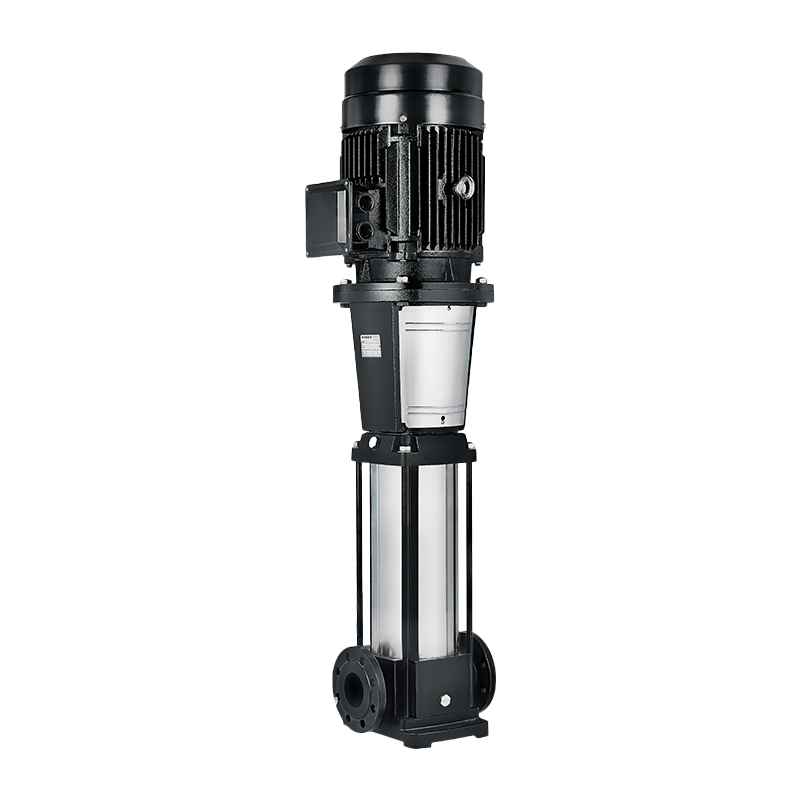
Horizontal multistage industrial diesel engine driven water pump
- This D series of pump is of sub-horizontal , multi-stage single-suction and centrifugal .The pump is efficient , reliable, and durable with low noise performance , easy maintenance andwide scope of usages .
- The D series single-suction multistage centrifugal pumps is widely used system of high-pressure run hot and cold water circulation and booster pumps in parallel water supply of the high-rise building,fire, boiler feed water and cooling water systems and a variety of irrigation fluid conveying.
- Application:long-distance water transferring boiling water feeding and transferring water system boosting agricultural irrigation mining water supply fire fighting offshore projects
- Used for transmission of water free of solid particles and temperature below 80℃ , or similar physical and chemical liquid . Suitable for mining ,mill and city water supply and drainage .
- Industrial Utilities, Irrigation and Agriculture, Mining industry, tem
 English
English عربى
عربى
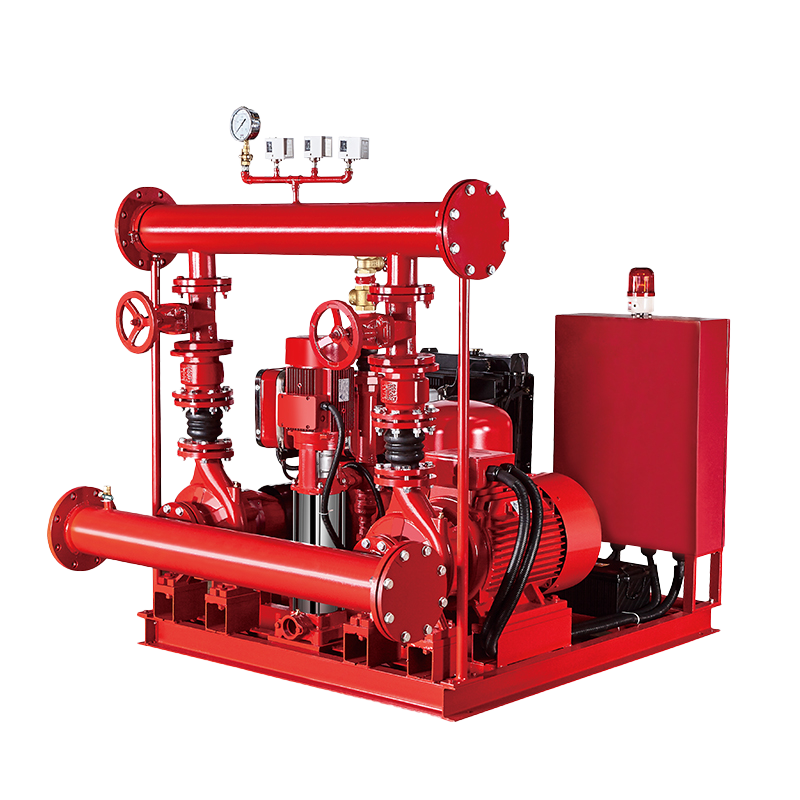 Fire Pump and System
Fire Pump and System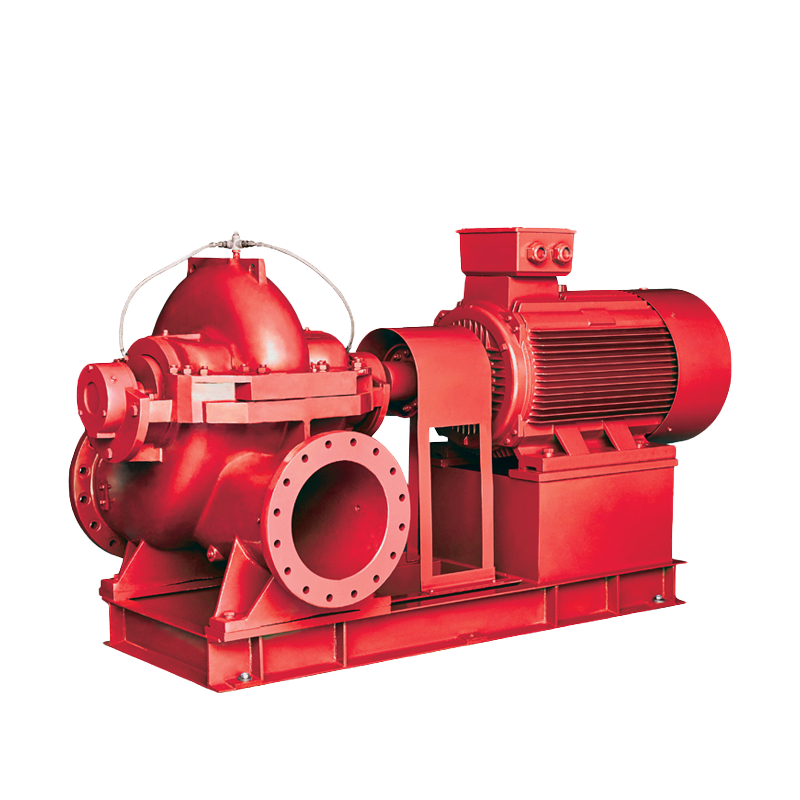 Split Case Pump
Split Case Pump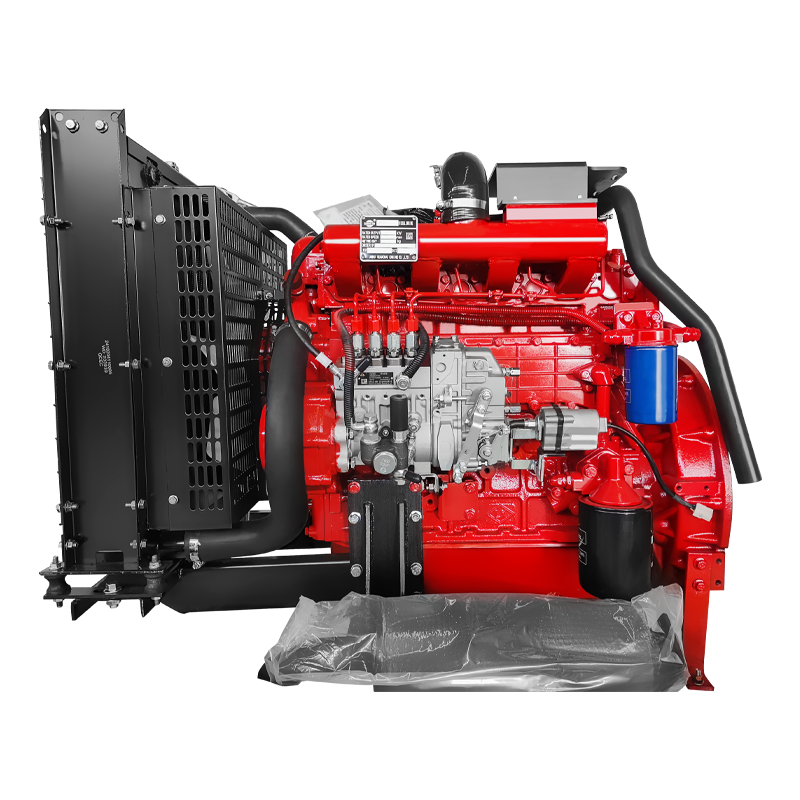 Engine and Pump
Engine and Pump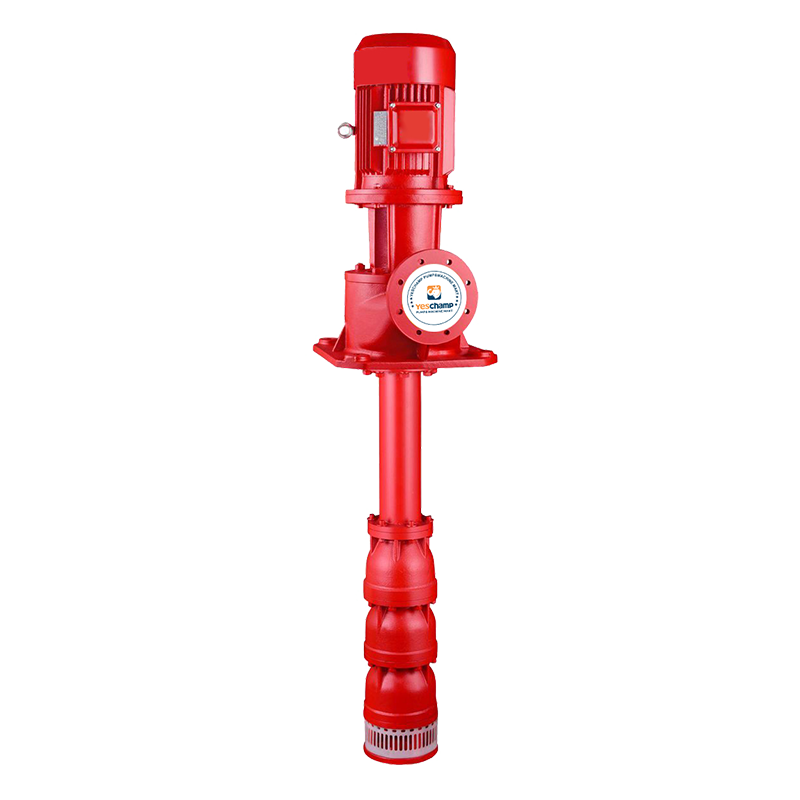 Long Shaft Pump
Long Shaft Pump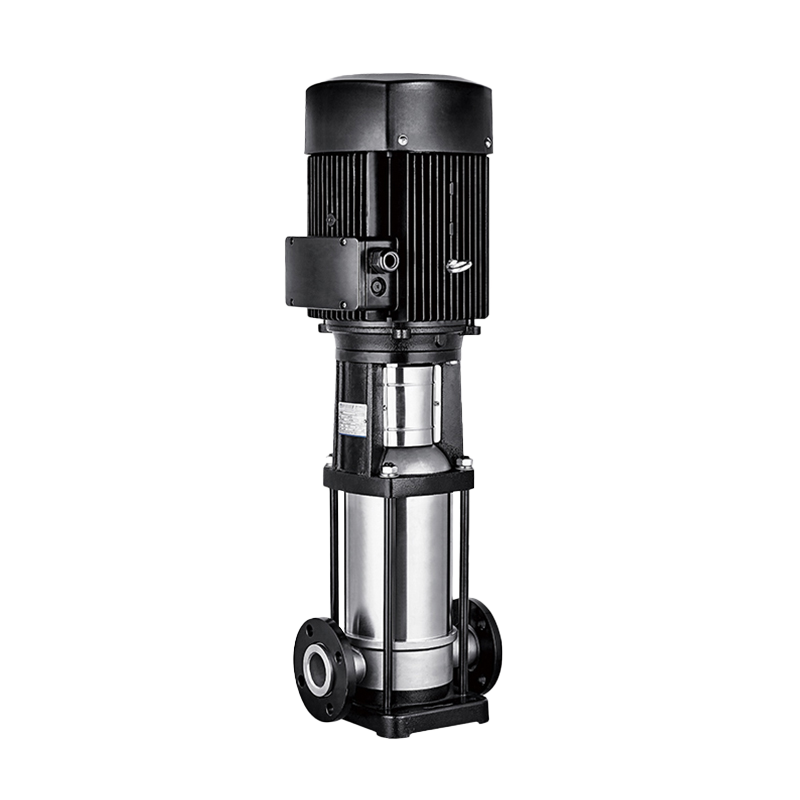 Multistage pump
Multistage pump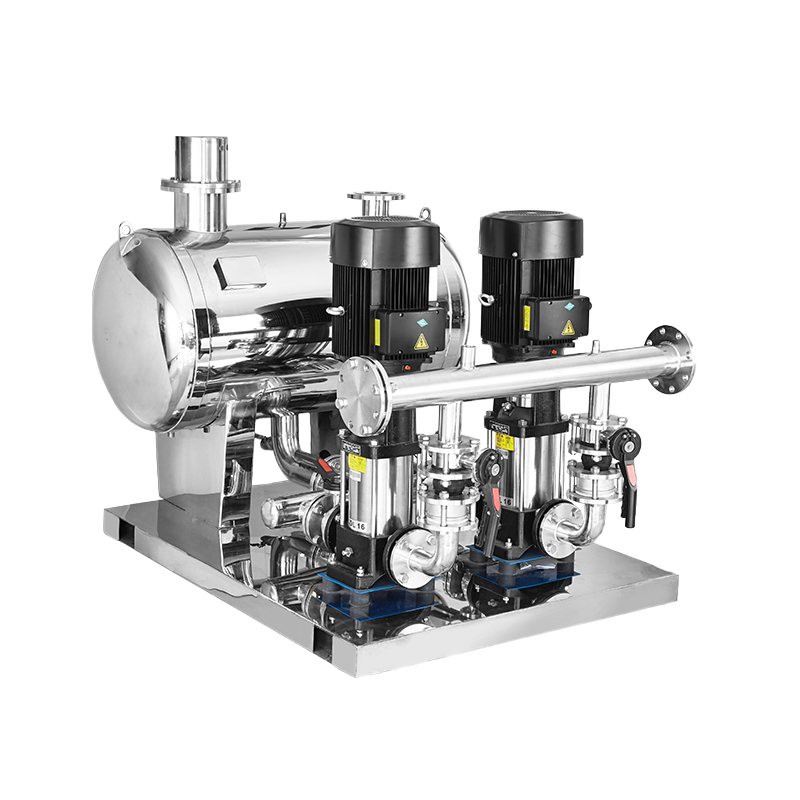 Water Supplier System
Water Supplier System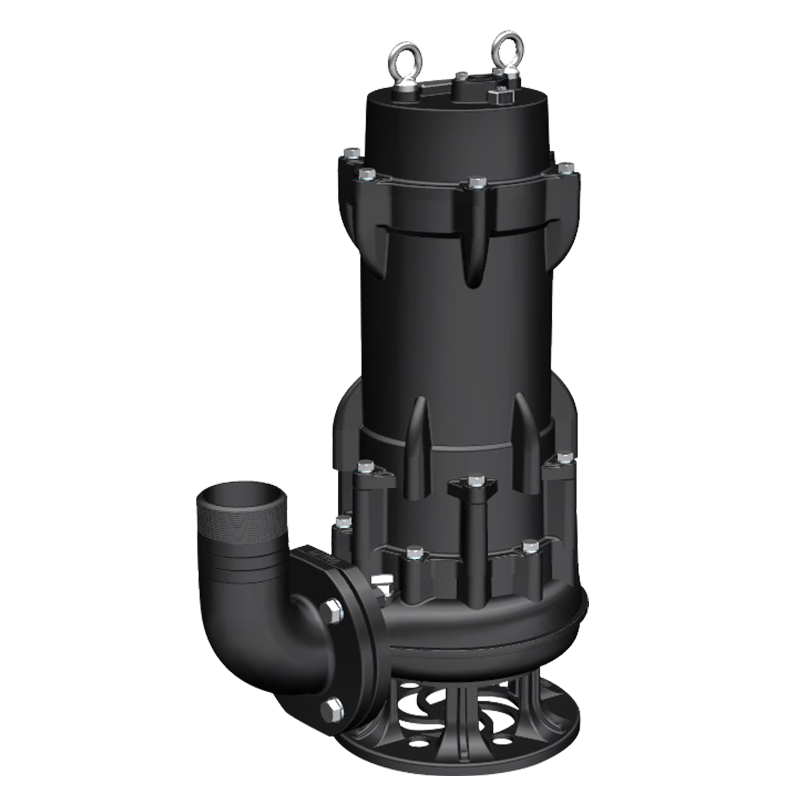 Sewage Pump
Sewage Pump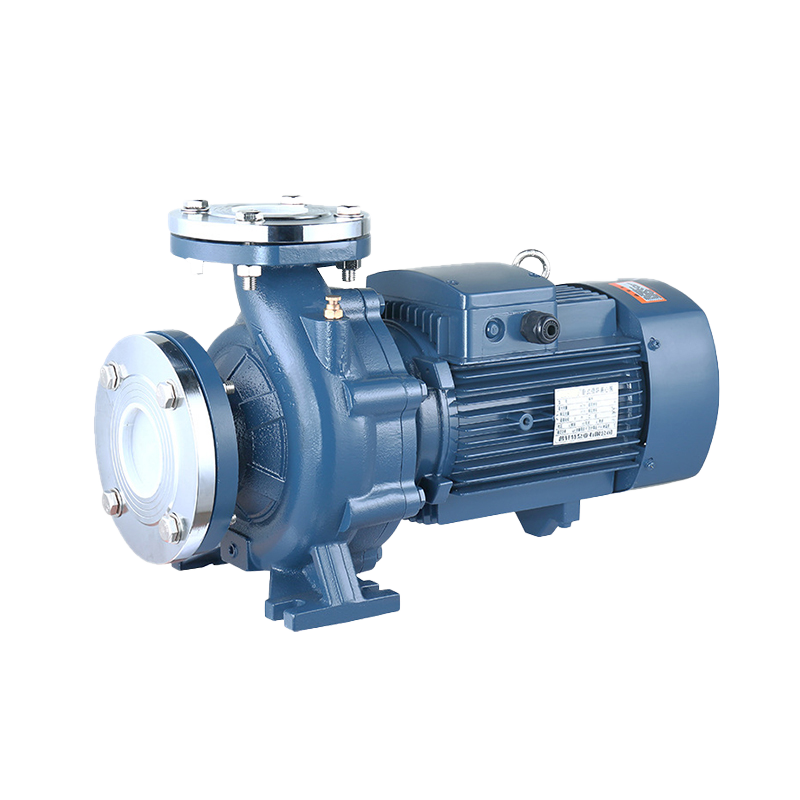 Industrial Pump
Industrial Pump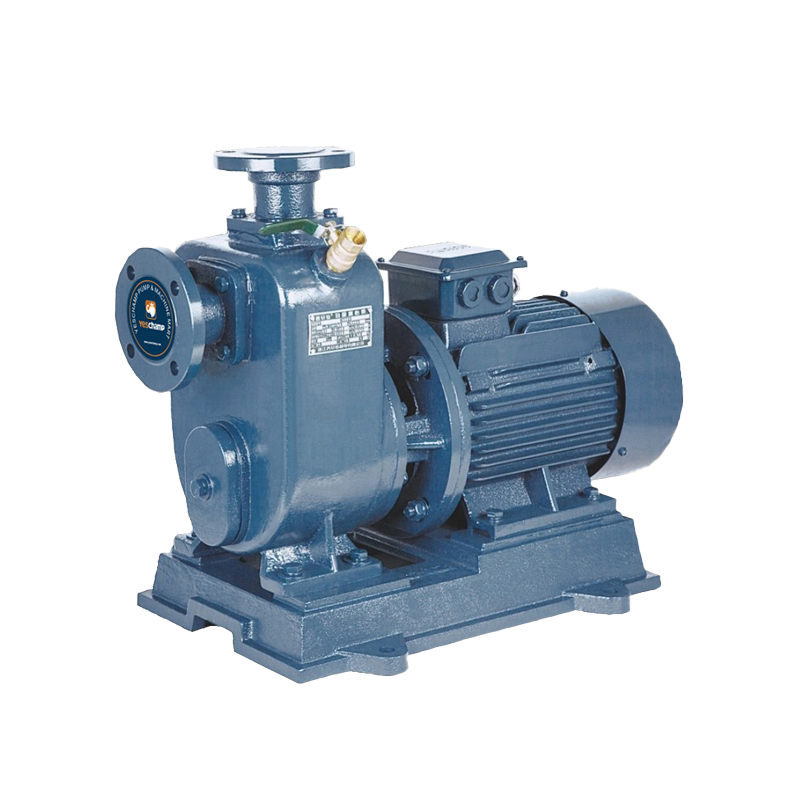 Self-Priming Pump
Self-Priming Pump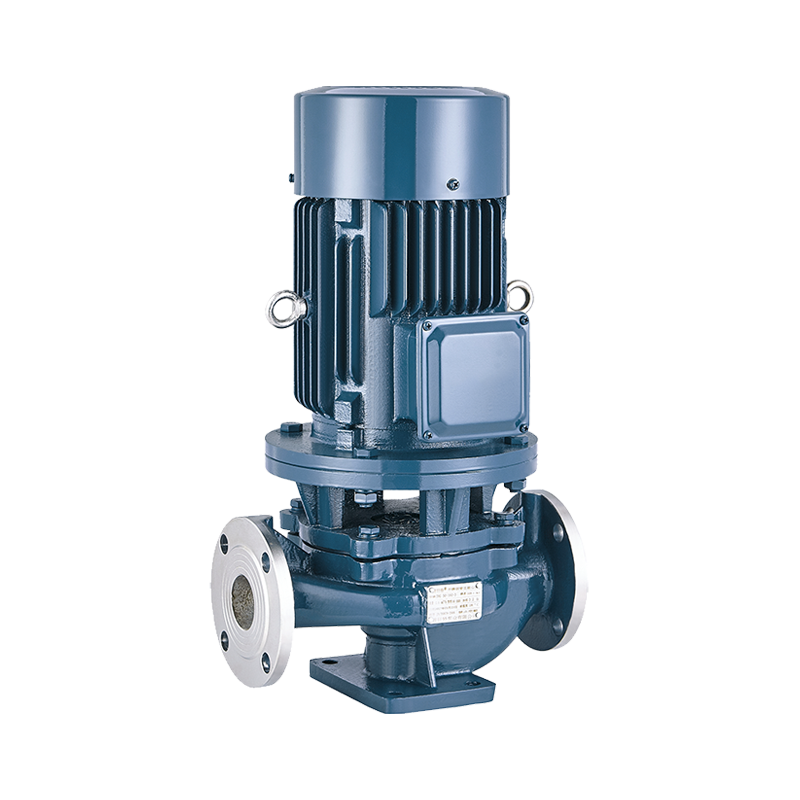 Inline Pump
Inline Pump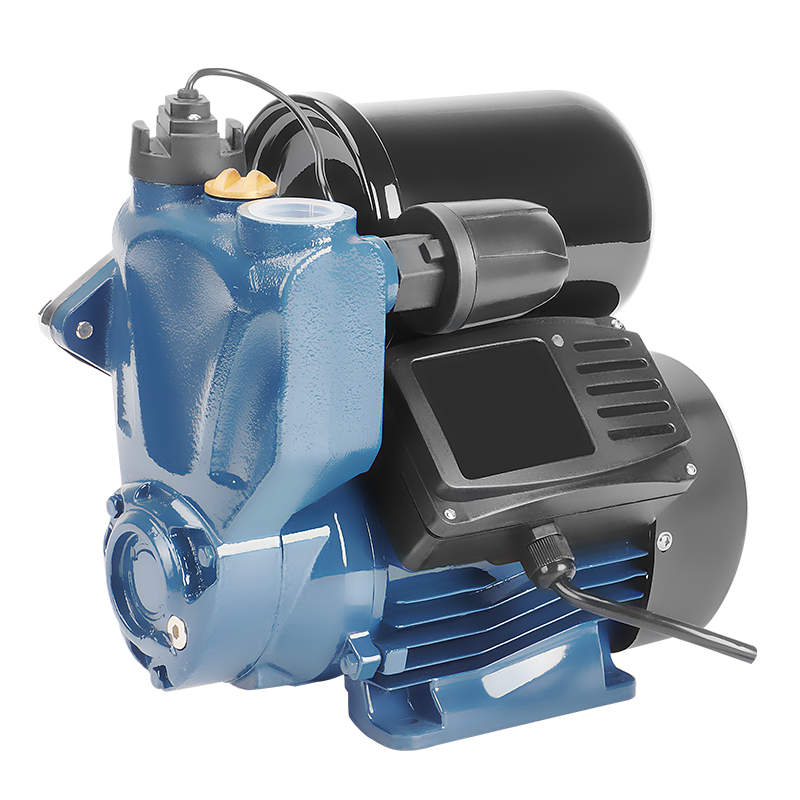 Domestic Pump
Domestic Pump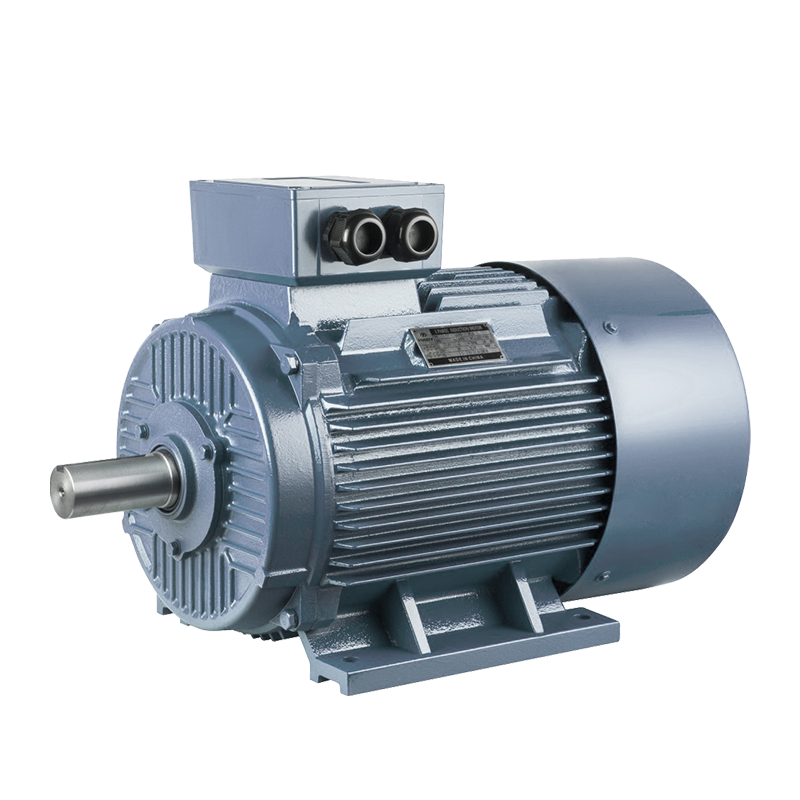 Electric Motor
Electric Motor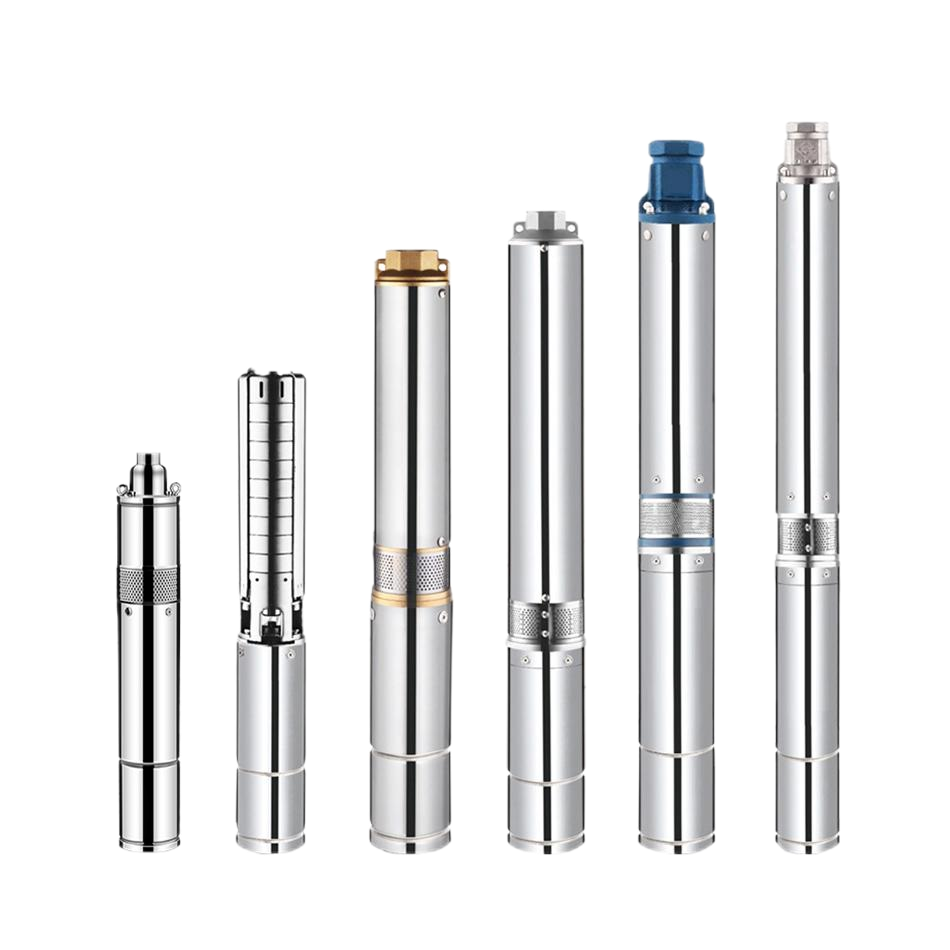 Borehole Pump
Borehole Pump