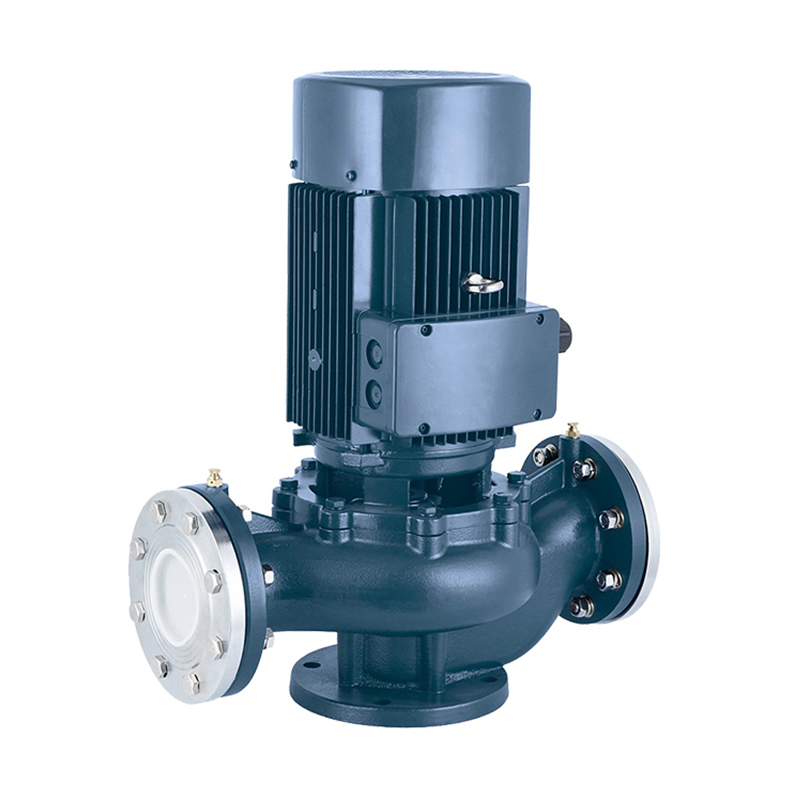
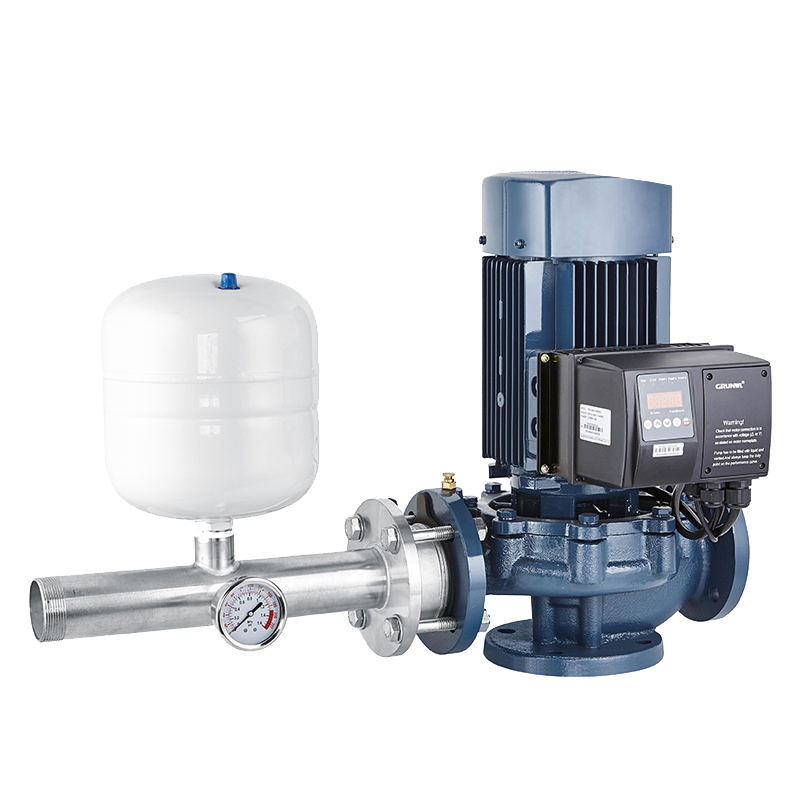
Vertical Multistage Pumps: The Ultimate Guide to Efficient Water Pressure Solutions
Vertical multistage pumps are high-performance pumping systems designed to provide constant water pressure for a variety of industrial, commercial, and residential applications. Known for their compact design, high energy efficiency, and ability to handle high-pressure demands, these pumps are widely used in water supply, irrigation, HVAC systems, and boiler water supply applications.
How do vertical multistage pumps work?
Vertical multistage pumps utilize multiple impellers (stages) connected in series within a single casing. Each impeller gradually increases water pressure, enabling the pump to efficiently achieve high pressures.
How it works:
Water intake:
Liquid enters through the suction port at the bottom.
Pressure boost:
As the water moves upward, each impeller stage increases pressure.
Discharge:
High-pressure water is discharged through the discharge port at the top.
This design makes vertical multistage pumps an ideal choice for applications requiring a steady, high-pressure water flow while saving space.
Structural Features of Vertical Multistage Pumps
1. Vertical Segmented Design:
The pump body consists of an inlet section, a midsection, guide vanes, and a discharge section. The vertical layout minimizes footprint and allows installation in underground tanks or confined spaces. Each section is bolted together for easy disassembly and maintenance.
2. Multi-Stage Impellers in Series:
The number of impellers is configured based on the required head (typically 2-13 stages). They are directly connected to the motor via a coupling to reduce transmission losses. Impeller materials can be selected from stainless steel (304/316) or alloy steel to accommodate different media.
3. Axial Force Balance:
A balancing drum or hydraulic balancing device absorbs of the axial force, with the remaining force being borne by angular contact ball bearings, reducing vibration and noise and extending bearing life.
4. Sealing and Bearing System:
The shaft seal can be either a packing seal or a mechanical seal. Mechanical seals are wear-resistant and leak-proof. The bearings utilize a combination of water-lubricated and angular contact ball bearings for smooth operation and low noise.
Application Scenarios for Vertical Multistage Pumps
1. High-Rise Building Water Supply:
Provides stable water pressure in high-rise buildings to meet residential and firefighting water needs. For example, in buildings over 30 stories, vertical multistage pumps can achieve a single pump head exceeding 120 meters.
2. Industrial Circulation Systems:
Used for transporting high-pressure cooling water, boiler feed water, and process fluids in the petrochemical industry, thermal power plants, and other fields. For example, in refineries, vertical multistage pumps can withstand high temperatures (150°C) and high pressures (4 MPa).
3. Agricultural Irrigation:
Pumps water from low-lying areas to high ground for farmland irrigation. For example, on large farms, a single pump can achieve a flow rate of 500 m³/h and a head exceeding 80 meters.
4. Municipal Water Supply:
Enables long-distance, high-head water transportation within urban pipeline networks to ensure water demand. For example, in interregional water transfer projects, vertical multistage pumps can operate continuously for over 2,000 hours without failure.
How do I choose the right vertical multistage pump?
When selecting a pump, consider the following factors:
Flow rate (GPM/LPM):
Meet your system's water needs.
Pressure requirement (PSI/Bar):
Ensure adequate pressure for your application.
Material compatibility:
Stainless steel for corrosive fluids, cast iron for clean water.
Motor power (HP/kW):
Meet your operating efficiency needs.
Certifications:
Find pumps that meet ISO, ANSI, or other industry standards.
Vertical multistage pumps are a choice for applications requiring high pressure, energy savings, and space optimization. Whether for industrial, commercial, or residential applications, choosing the right pump ensures long-term reliability and performance.
 English
English عربى
عربى
 Fire Pump and System
Fire Pump and System Split Case Pump
Split Case Pump Engine and Pump
Engine and Pump Long Shaft Pump
Long Shaft Pump Multistage pump
Multistage pump Water Supplier System
Water Supplier System Sewage Pump
Sewage Pump Industrial Pump
Industrial Pump Self-Priming Pump
Self-Priming Pump Inline Pump
Inline Pump Domestic Pump
Domestic Pump Electric Motor
Electric Motor Borehole Pump
Borehole Pump