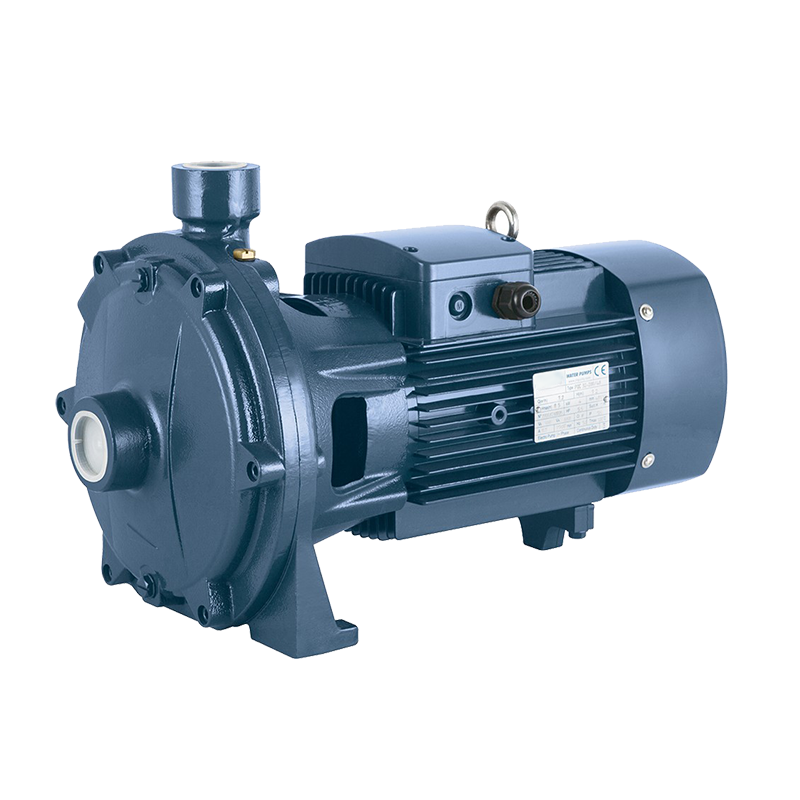
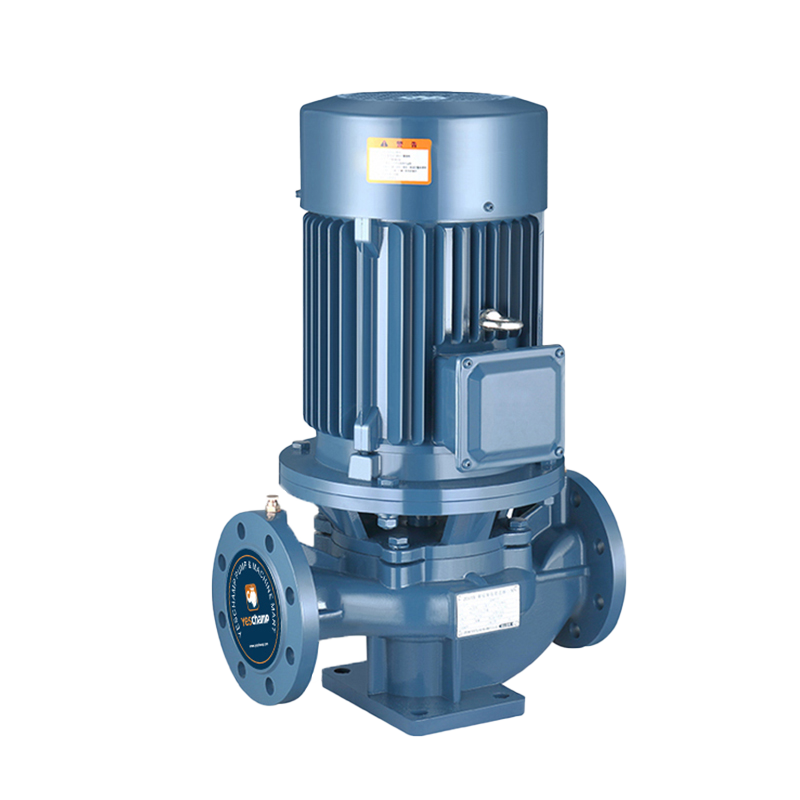
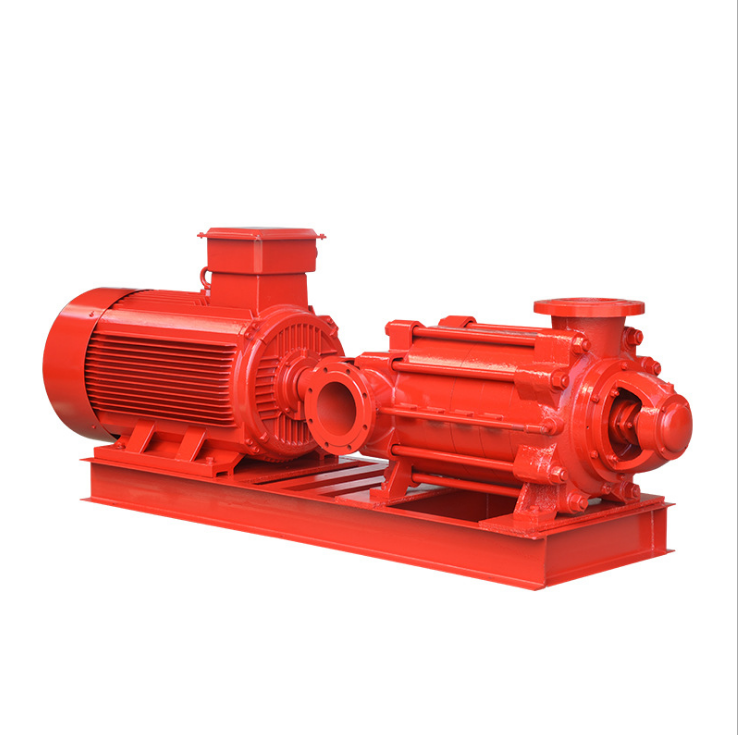
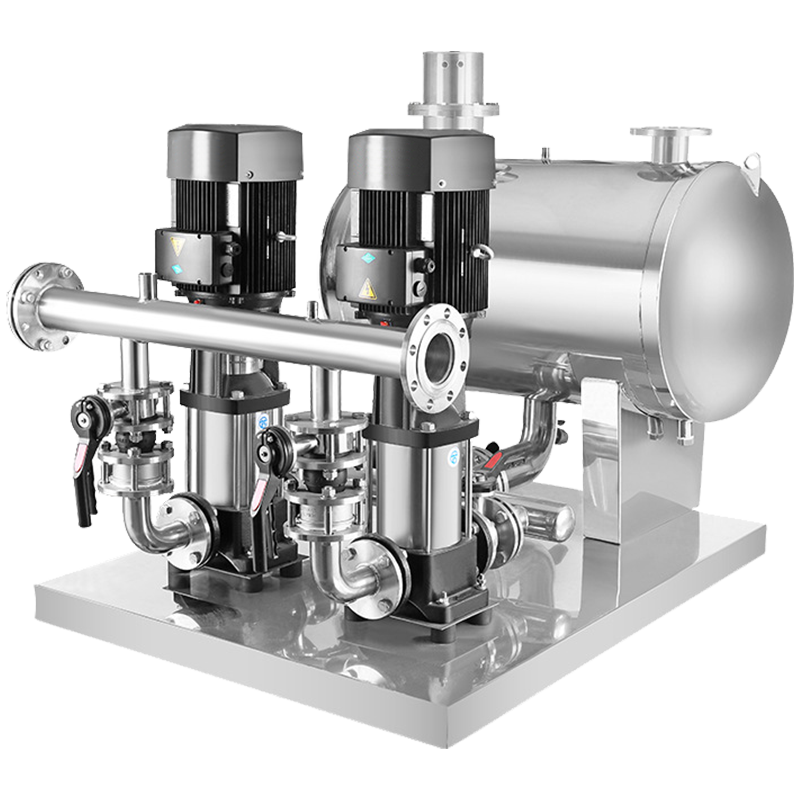
The Ultimate Guide to Pipeline Pumps: Types, Applications, and Benefits
Pipeline pump is a type of single-suction single-stage or multi-stage centrifugal pump, which is a vertical structure. Because its inlet and outlet are on the same straight line and have the same inlet and outlet diameters, it resembles a section of pipeline and can be installed at any position of the pipeline, so it is named pipeline pump (also known as booster pump). Structural features: It is a single-suction single-stage centrifugal pump, with the inlet and outlet being the same and on the same straight line, perpendicular to the axis centerline, and a vertical pump.
Working principle of pipeline pump
The working principle of pipeline pump is based on the continuity equation and Bernoulli equation in fluid mechanics. When the motor drives the pump shaft to rotate, the impeller rotates accordingly, generating centrifugal force, throwing water from the center of the impeller to the periphery, forming a low-pressure area, thereby sucking in the water source. At the same time, the high-pressure area outside the impeller pushes the water to the outlet to achieve water transportation.
The flow rate and head of the pipeline pump can be controlled by adjusting the speed and blade angle of the impeller. In practical applications, the selection of pipeline pumps needs to comprehensively consider factors such as the system's flow rate, head, power, efficiency, etc. to ensure the stable and efficient operation of the water supply system.
Types of Pipeline Pumps
Pipeline pumps come in various designs, each suited for specific applications. The common types include:
1. Centrifugal Pumps
How They Work: Use rotational energy to move fluids through impellers.
Best For: High-flow, low-pressure applications like water supply and irrigation.
2. Reciprocating Pumps
How They Work: Use pistons or plungers to create pressure and move fluids.
Best For: High-pressure applications such as oil pipelines and hydraulic systems.
3. Diaphragm Pumps
How They Work: Utilize a flexible diaphragm to displace liquid.
Best For: Handling corrosive or viscous fluids in chemical processing.
4. Submersible Pumps
How They Work: Operate underwater, pushing fluids to the surface.
Best For: Drainage, sewage systems, and deep-well extraction.
5. Multistage Pumps
How They Work: Use multiple impellers to increase pressure in stages.
Best For: Long-distance pipeline transportation, such as in oil refineries.
Key Applications of Pipeline Pumps
Pipeline pumps are widely used across industries, including:
Water & Wastewater Treatment: Ensuring smooth water distribution and sewage management.
Oil & Gas Industry: Transporting crude oil, refined products, and natural gas.
Chemical Processing: Handling aggressive and hazardous liquids safely.
Agriculture: Supporting irrigation and drainage systems.
Power Plants: Circulating cooling water and other fluids.
Pipeline pump maintenance
1. Clean all parts to be installed.
2. Install the mechanical seal on the motor main shaft, and add a small amount of clean turbine oil or No. 20 engine oil to the matching surface of the dynamic and static rings of the mechanical seal.
3. Install the impeller and tighten it with the impeller nut.
Pipeline pumps play a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient fluid transportation across multiple industries. By understanding the different types, applications, and selection criteria, you can choose the pump for your specific needs.
 English
English عربى
عربى
 Fire Pump and System
Fire Pump and System Split Case Pump
Split Case Pump Engine and Pump
Engine and Pump Long Shaft Pump
Long Shaft Pump Multistage pump
Multistage pump Water Supplier System
Water Supplier System Sewage Pump
Sewage Pump Industrial Pump
Industrial Pump Self-Priming Pump
Self-Priming Pump Inline Pump
Inline Pump Domestic Pump
Domestic Pump Electric Motor
Electric Motor Borehole Pump
Borehole Pump