Understanding Turbine Pumps: A Comprehensive Guide
What is a Turbine Pump?
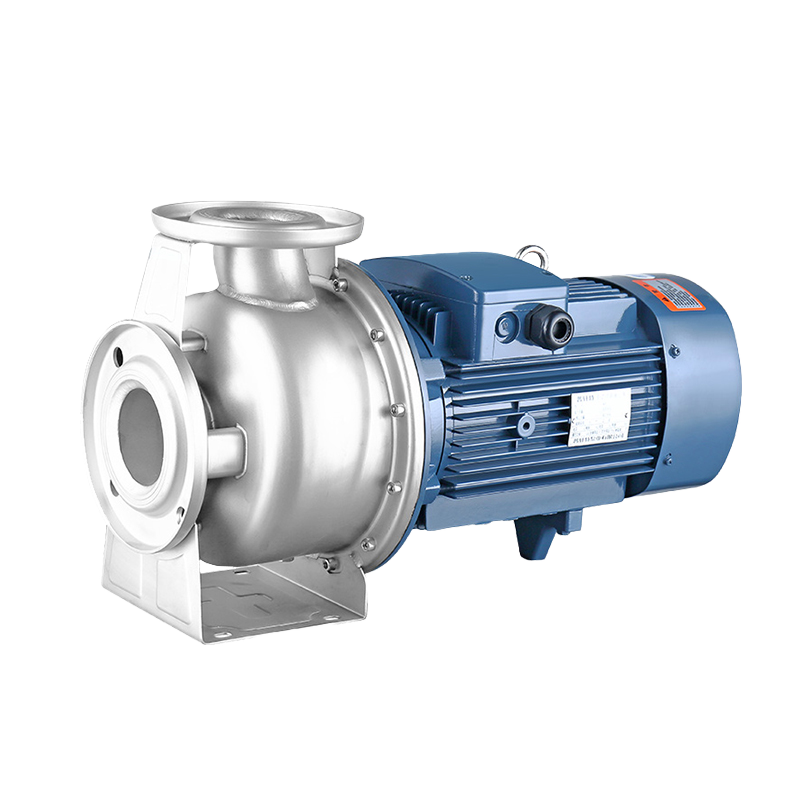
Vertical turbine pump are suitable for conveying various corrosive media such as particles, high viscosity, strong acid, alkali, salt, strong oxidant, etc. The new submersible pump is suitable for conveying various lightweight media such as flammable and explosive. The shell, outlet pipe and flow-through parts of the traditional submersible pump are all made of corrosion-resistant materials. The motor part is placed on the liquid surface and the pump part is placed below the liquid surface. It has the characteristics of strong corrosion resistance, no blockage, and high temperature resistance. The pump body, motor and flow-through parts of the new submersible pump are all made of special materials. The motor part and the pump part are coaxially connected as a whole and placed below the liquid surface. It has the characteristics of maintenance-free, high explosion-proof, zero-zone use, and low energy consumption.
How Turbine Pumps Work
• Multi-Stage Configurations (5-50 stages) generate heads to 1000+ feet
• Closed Impeller Design achieves 85-92% hydraulic efficiency
• Column & Bowl Assembly allows deep setting in wells/boreholes
• Oil/Grease Lubrication options for different water conditions
Applications of Turbine Pumps
Turbine pumps are versatile and used in various applications, including:
Water Supply Systems:
Ideal for municipal water systems due to their ability to handle large volumes.
Irrigation:
Commonly used in agricultural applications to ensure efficient water distribution.
Chemical Processing:
Suitable for transferring corrosive or viscous fluids.
Wastewater Management:
Employed in sewage and wastewater treatment plants for effective fluid movement.
 English
English عربى
عربى
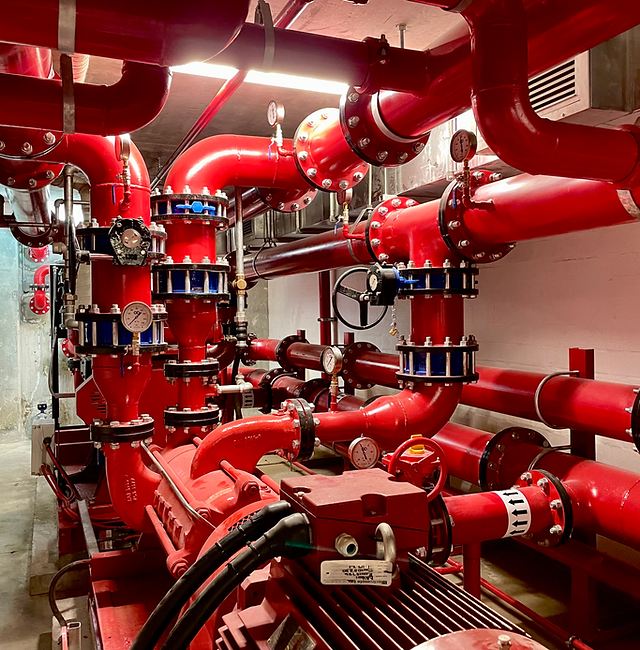
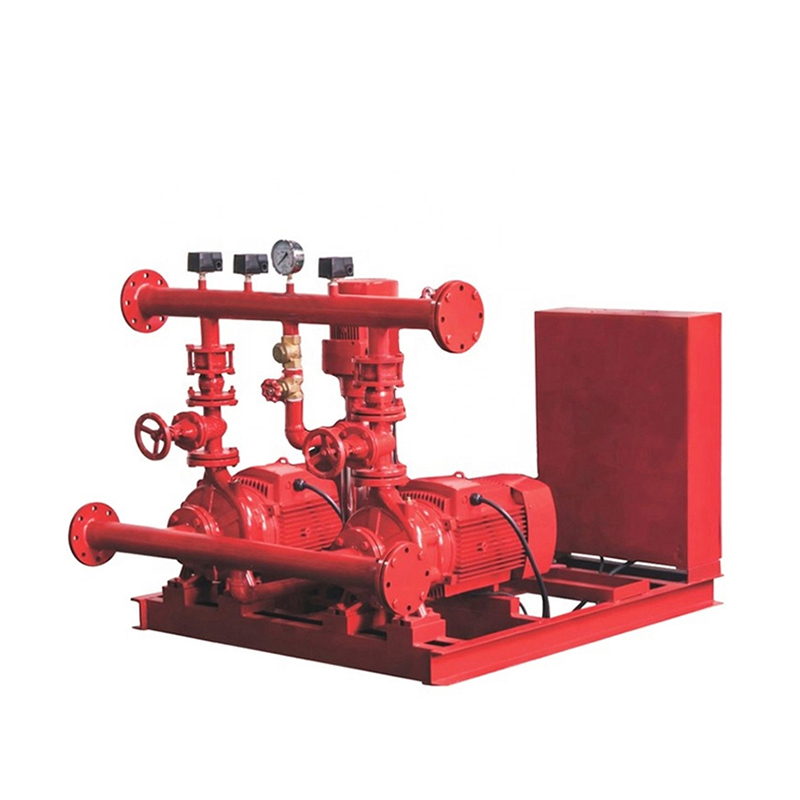
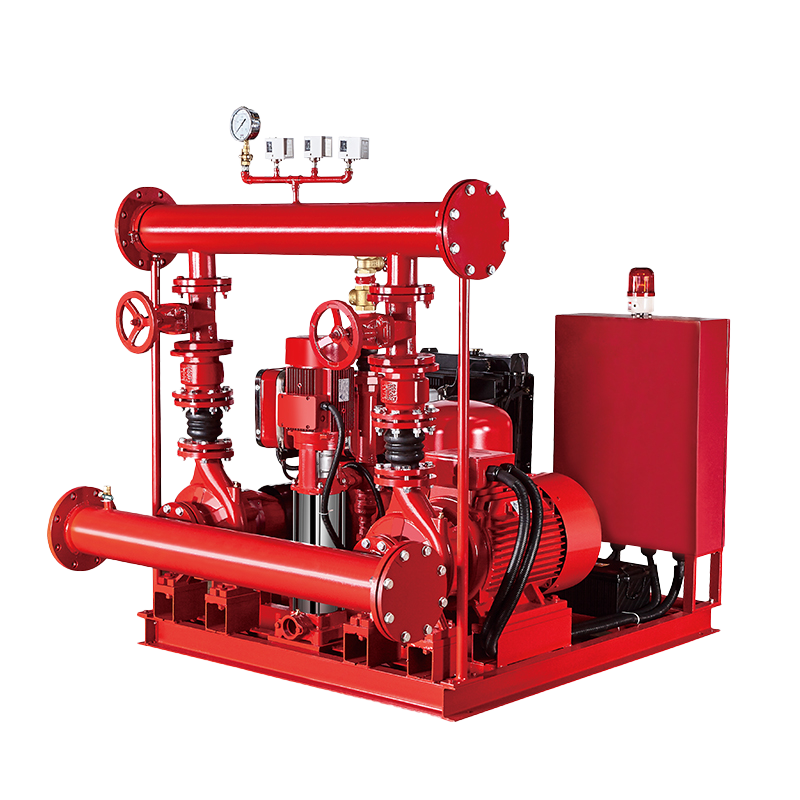 Fire Pump and System
Fire Pump and System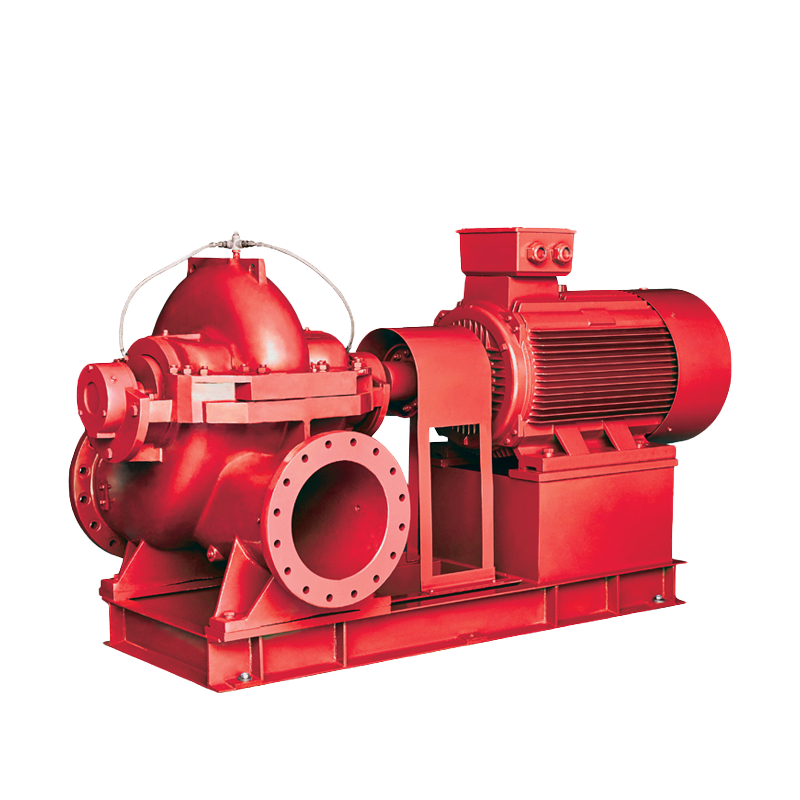 Split Case Pump
Split Case Pump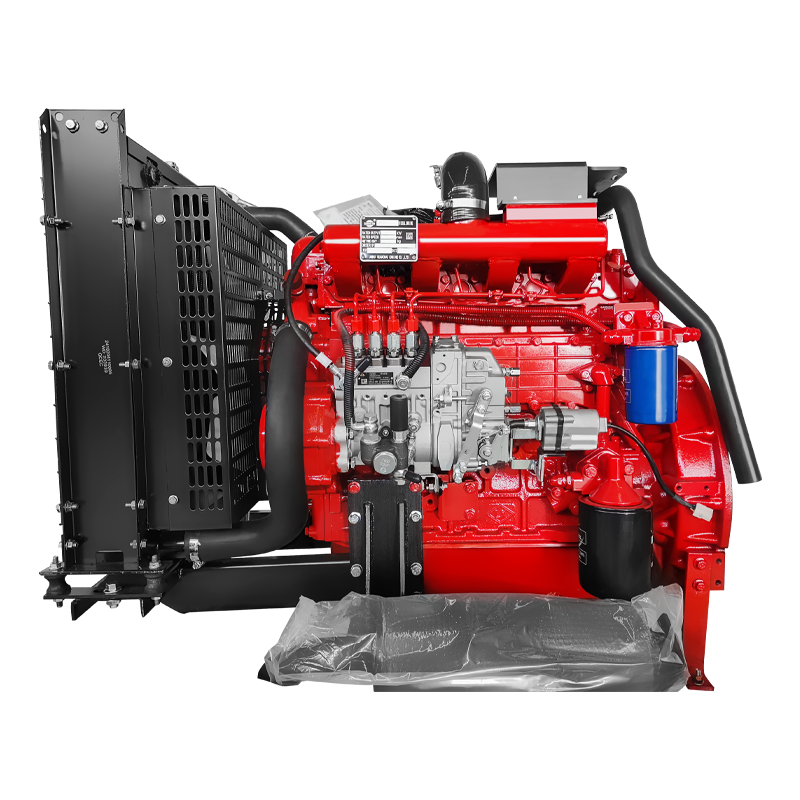 Engine and Pump
Engine and Pump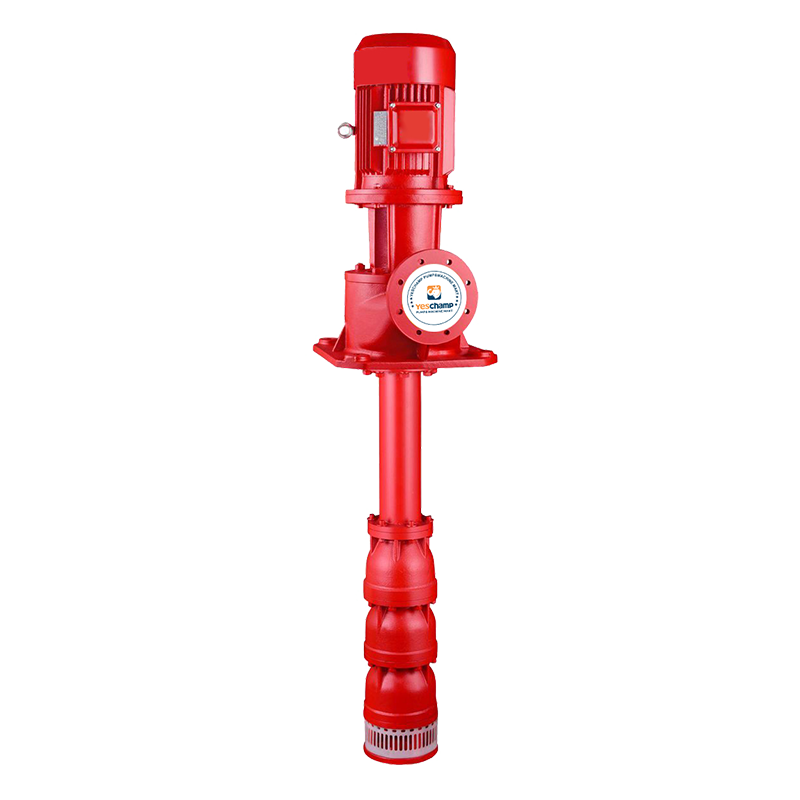 Long Shaft Pump
Long Shaft Pump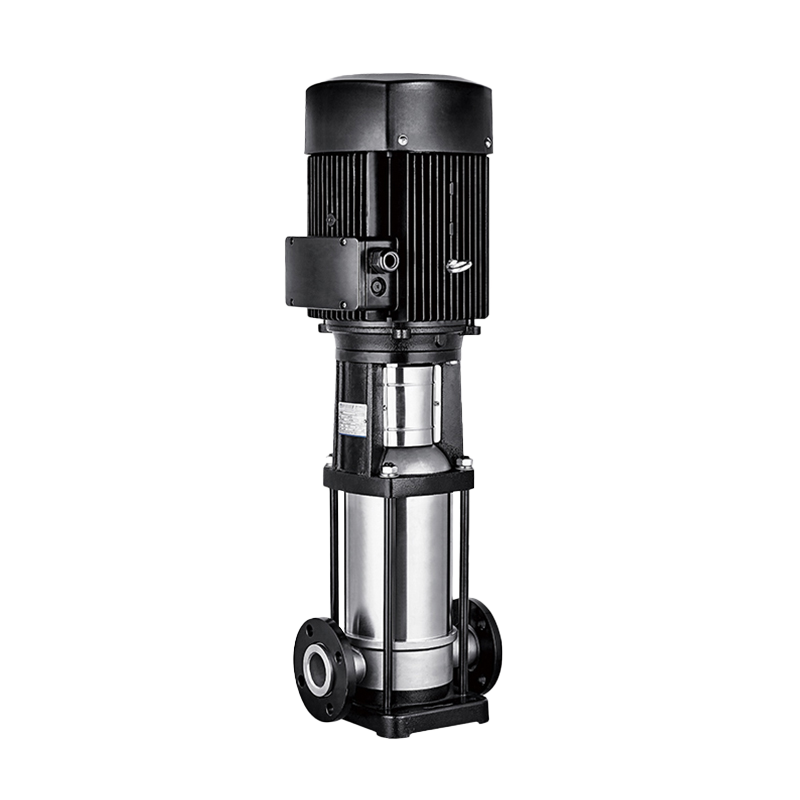 Multistage pump
Multistage pump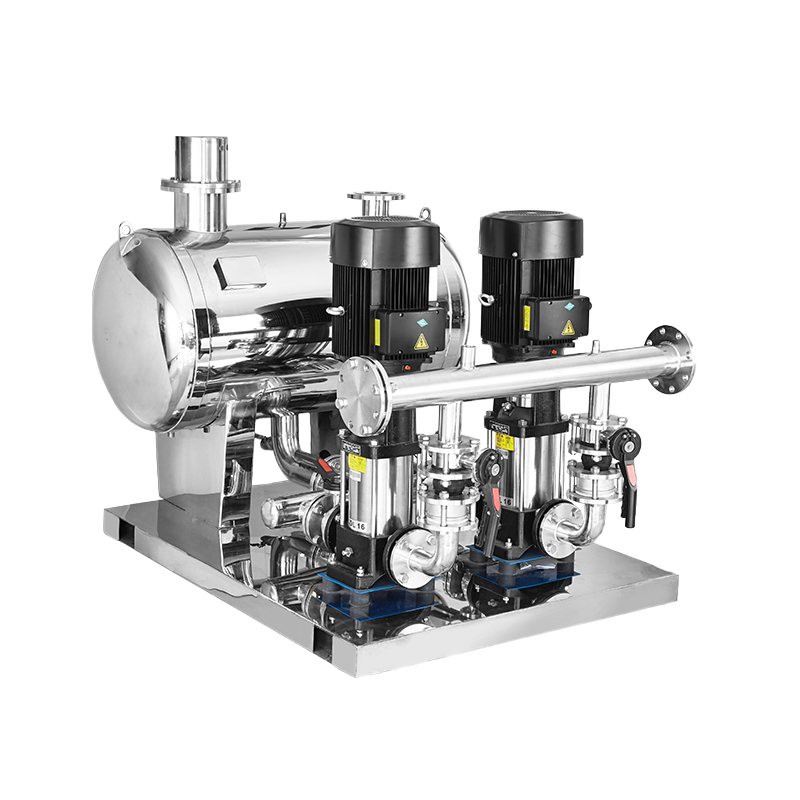 Water Supplier System
Water Supplier System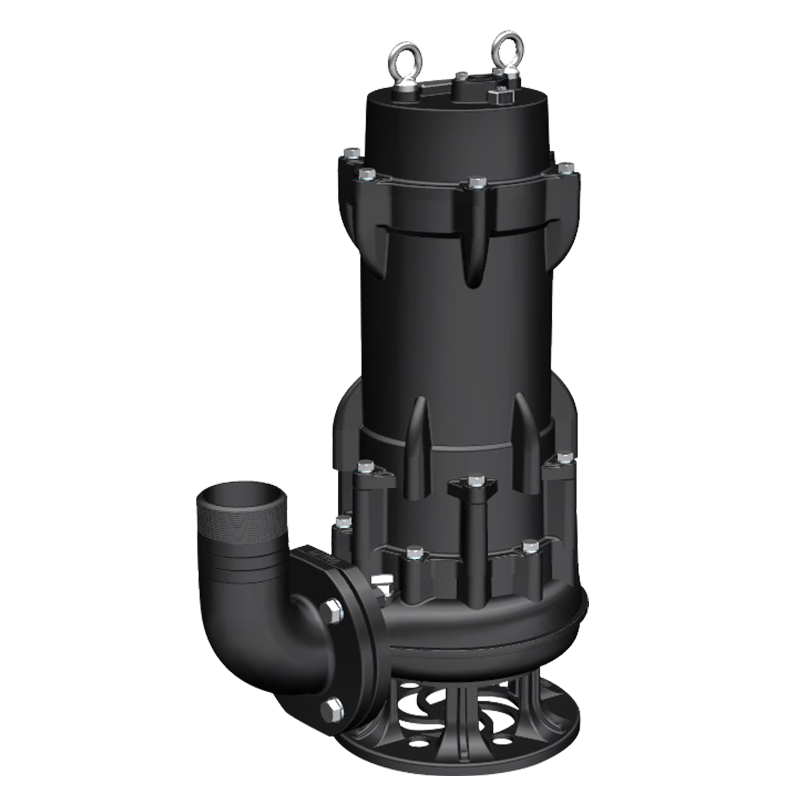 Sewage Pump
Sewage Pump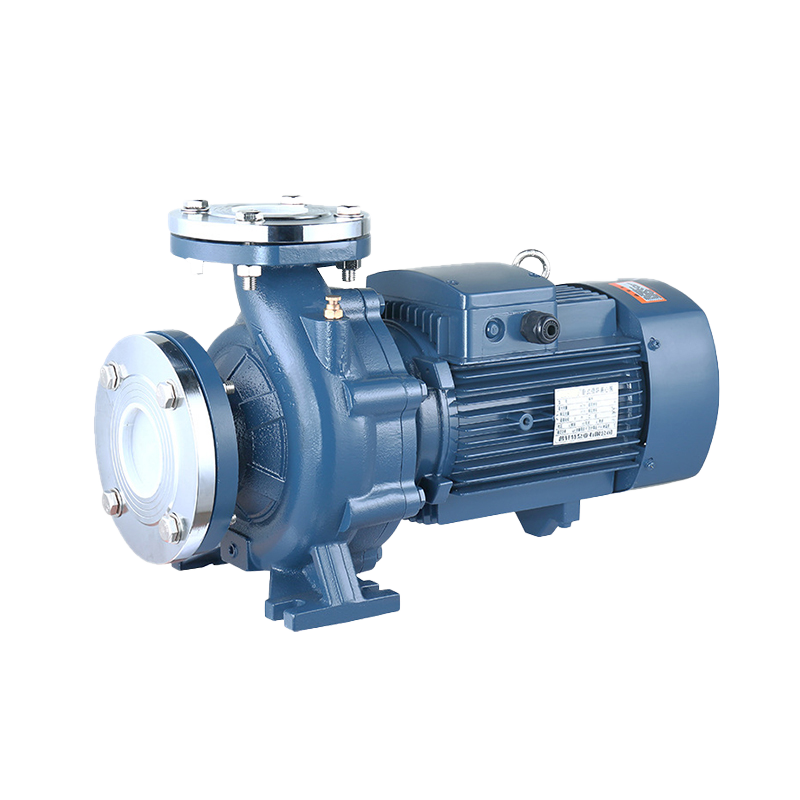 Industrial Pump
Industrial Pump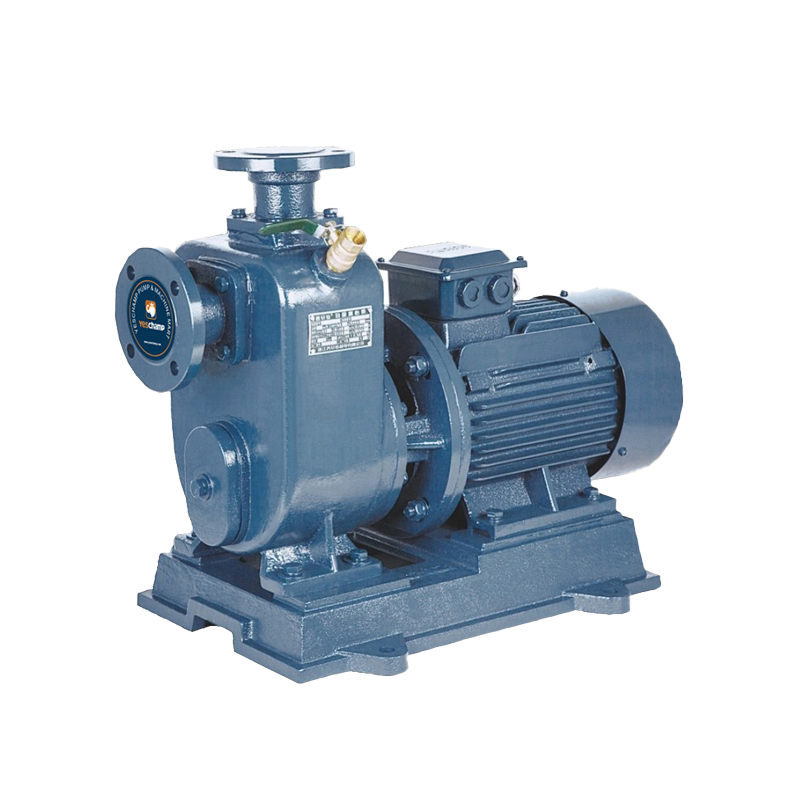 Self-Priming Pump
Self-Priming Pump Inline Pump
Inline Pump Domestic Pump
Domestic Pump Electric Motor
Electric Motor Borehole Pump
Borehole Pump