Water Supply System: The Complete Guide to Efficient Water Distribution
A water supply system is a critical infrastructure designed to collect, treat, store, and distribute water to meet the needs of residential, industrial, agricultural, and commercial users. Ensuring a reliable and efficient water supply is essential for public health, economic development, and environmental sustainability.
What Is a Water Supply System?
A water supply system is a network of infrastructure and equipment that ensures the delivery of clean water from its source to end users. It includes processes such as water collection, treatment, storage, and distribution.
Water supply systems are essential in urban and rural settings to provide safe drinking water, support industrial processes, irrigate crops, and maintain sanitation standards.

Components of a Water Supply System
A water supply system consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in ensuring efficient water delivery:
1. Water Sources
Surface Water: Includes rivers, lakes, and reservoirs.
Groundwater: Extracted from aquifers using wells or boreholes.
2. Intake Structures
Facilities designed to collect water from natural sources and direct it into the supply system.
3. Water Treatment Plants
Facilities where water is purified through processes like filtration, sedimentation, disinfection, and chemical treatment.
4. Storage Tanks and Reservoirs
Used to store treated water and regulate pressure within the distribution system.
5. Pumping Stations
Essential for moving water through the system, especially in areas with varying elevations.
6. Distribution Network
A network of pipelines, valves, and meters that delivers water to end users.
7. Control Systems
Automated systems that monitor and regulate water flow, pressure, and quality.

Benefits of a Reliable Water Supply System
Investing in a well-designed water supply system offers several advantages:
1. Access to Clean Water
Ensures safe and hygienic water for drinking, cooking, and sanitation.
2. Improved Public Health
Reduces the risk of waterborne diseases by providing treated water.
3. Economic Growth
Supports industries, agriculture, and businesses, driving economic development.
4. Enhanced Quality of Life
Provides water for daily needs, improving living standards and convenience.
5. Environmental Sustainability
Promotes the efficient use of water resources and reduces wastage.
6. Reliable Water Pressure
Maintains consistent water flow for residential and industrial users.
A water supply system is the backbone of modern society, ensuring the efficient delivery of clean water for drinking, sanitation, agriculture, and industry. With components like water sources, treatment plants, and distribution networks, these systems play a vital role in public health, economic growth, and environmental sustainability.
Designing and maintaining an efficient water supply system requires careful planning, regular maintenance, and the integration of advanced technologies to meet growing demands and challenges.
 English
English عربى
عربى
 Fire Pump and System
Fire Pump and System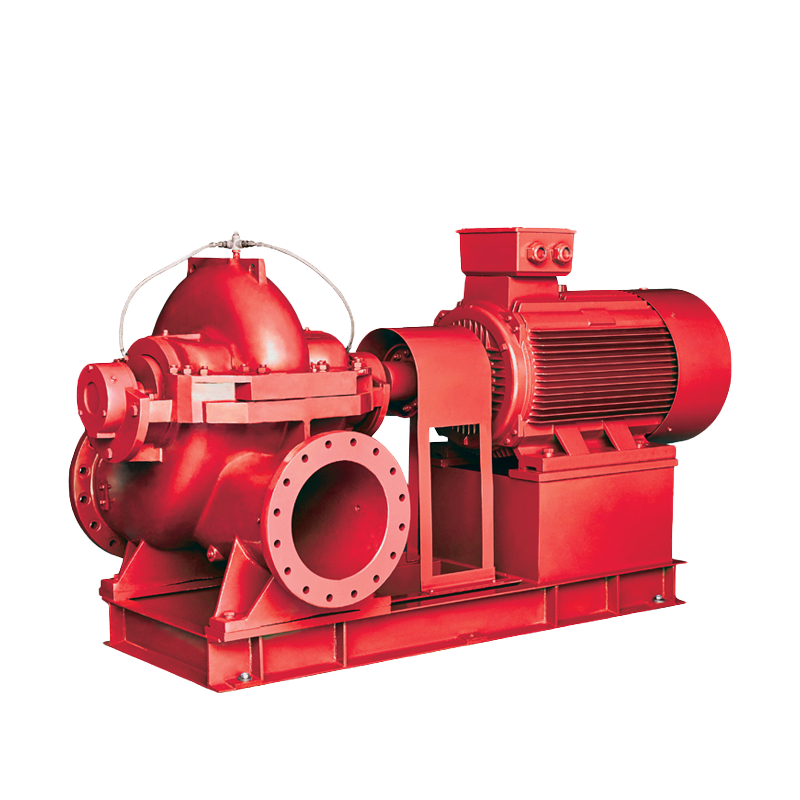 Split Case Pump
Split Case Pump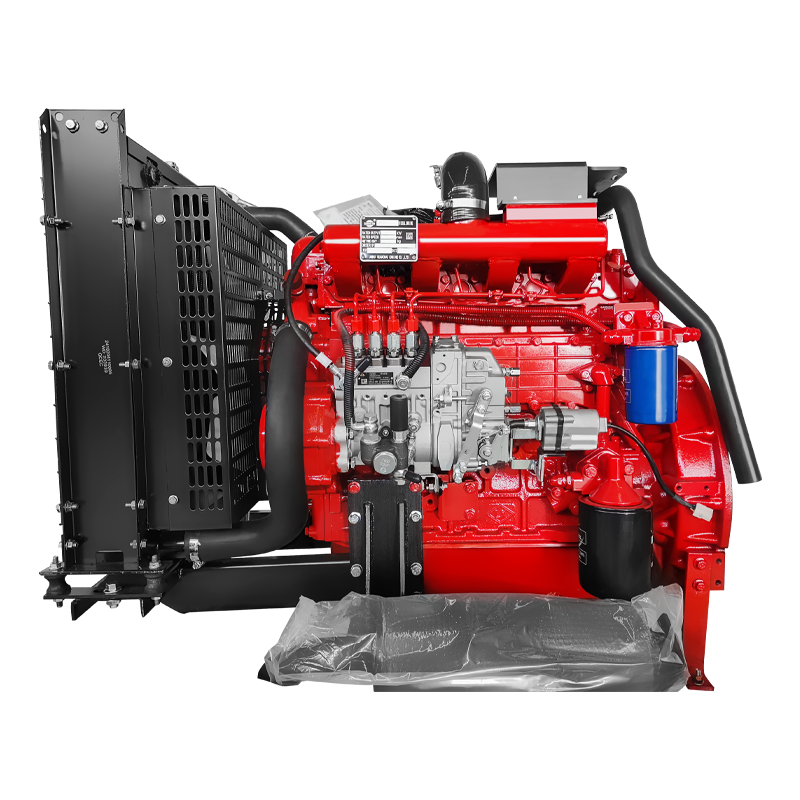 Engine and Pump
Engine and Pump Long Shaft Pump
Long Shaft Pump Multistage pump
Multistage pump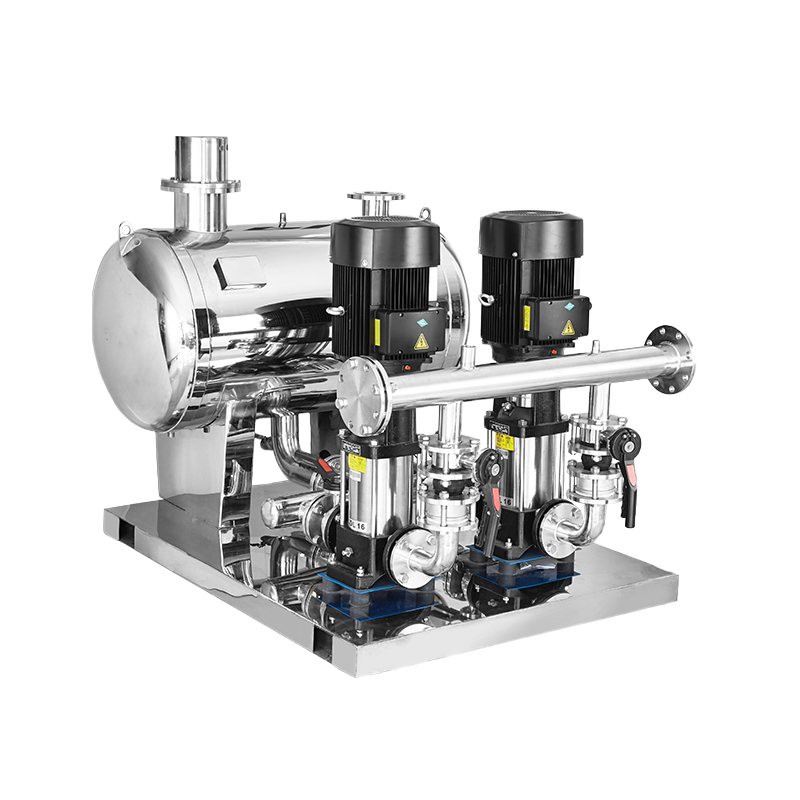 Water Supplier System
Water Supplier System Sewage Pump
Sewage Pump Industrial Pump
Industrial Pump Self-Priming Pump
Self-Priming Pump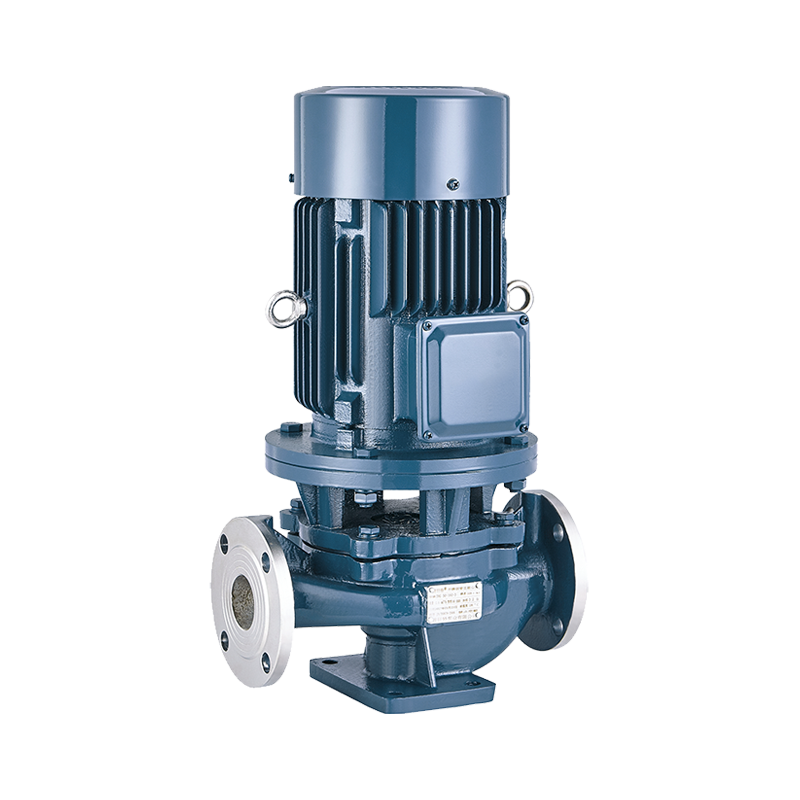 Inline Pump
Inline Pump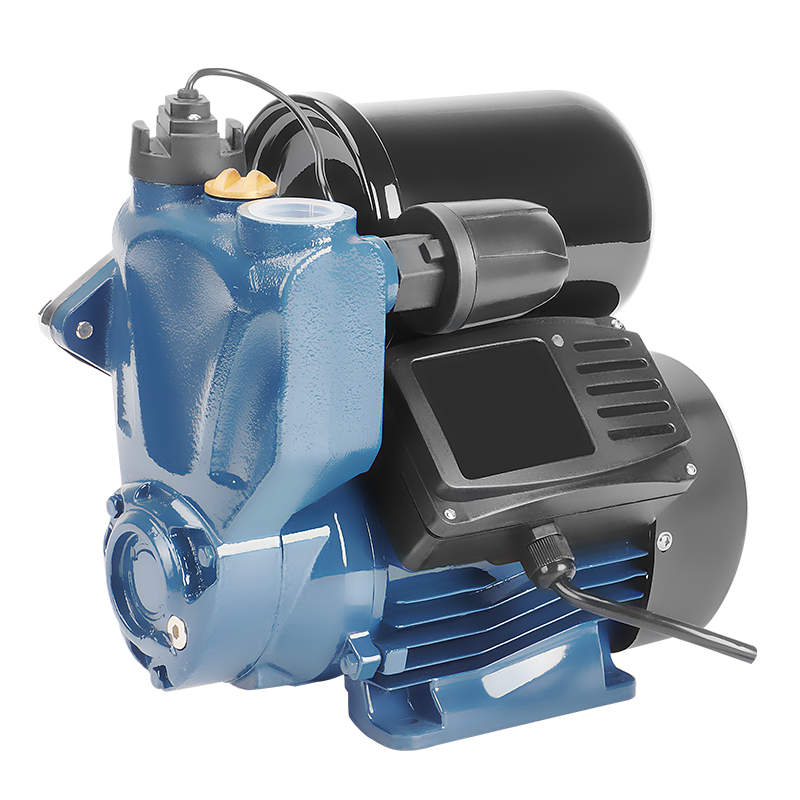 Domestic Pump
Domestic Pump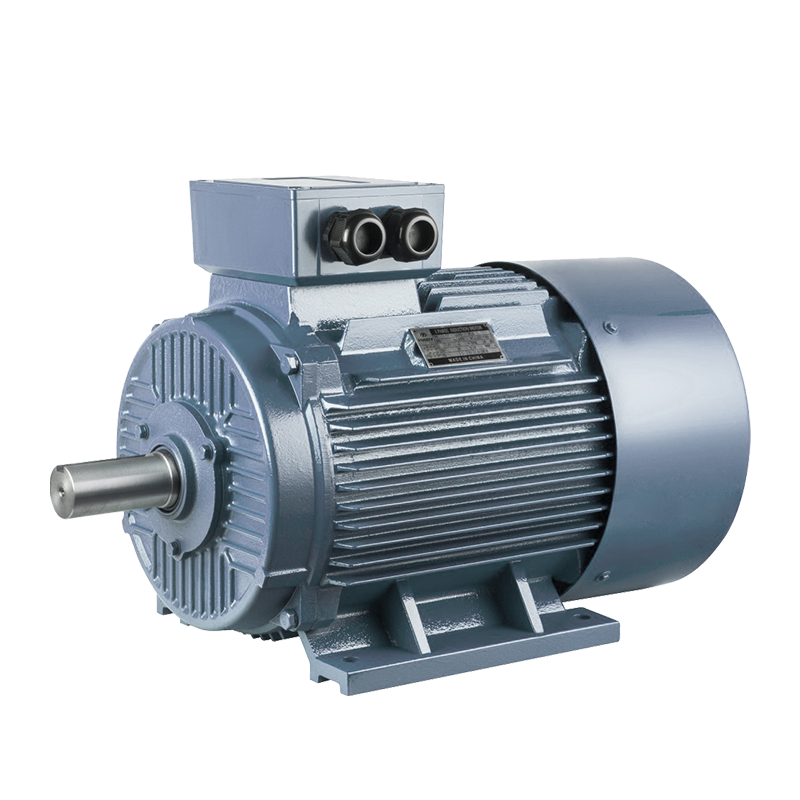 Electric Motor
Electric Motor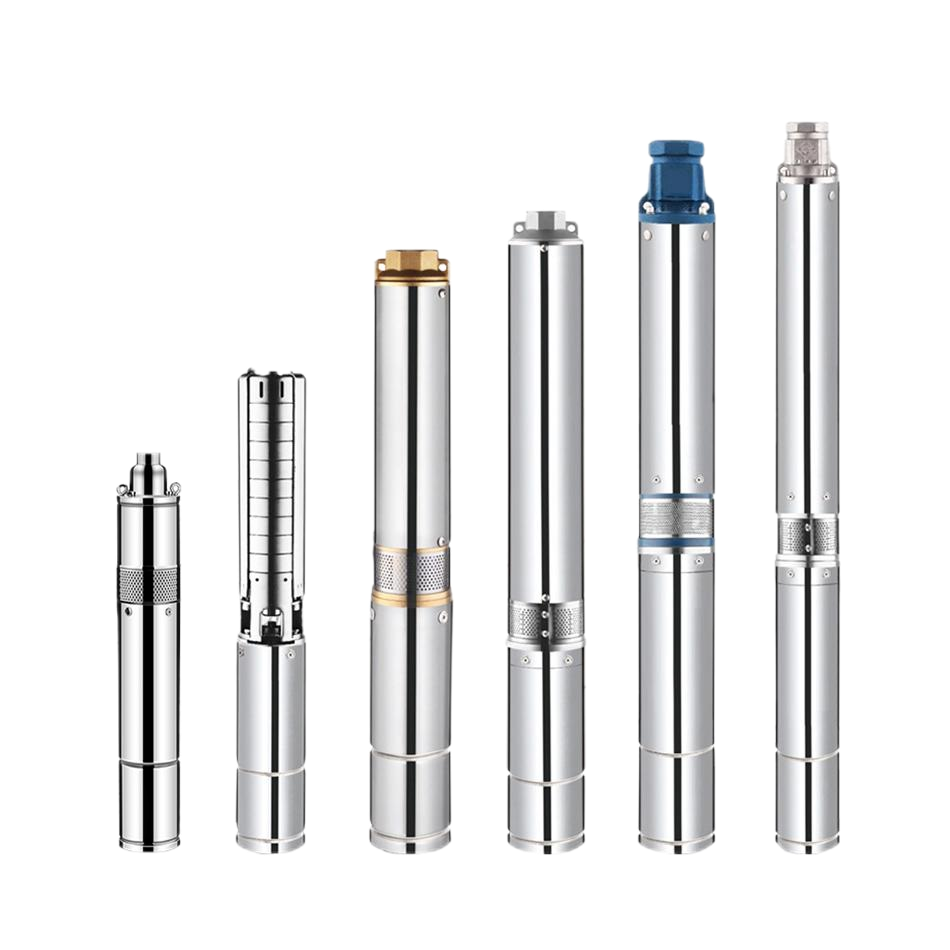 Borehole Pump
Borehole Pump